建造者模式使用也有一段时间了,之前对它的概念也是云里雾里的,只是会用,却也拿不定主意什么时候用好,今天突然间有所领悟,特记录之。首先说说它的定义,基本上看到所有关于建造者模式的介绍大概都是这样说的:
意图:将一个复杂的构建与其表示相分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。
主要解决:主要解决在软件系统中,有时候面临着"一个复杂对象"的创建工作,其通常由各个部分的子对象用一定的算法构成;由于需求的变化,这个复杂对象的各个部分经常面临着剧烈的变化,但是将它们组合在一起的算法却相对稳定。
何时使用:一些基本部件不会变,而其组合经常变化的时候。
如何解决:将变与不变分离开。
关键代码:建造者:创建和提供实例,导演:管理建造出来的实例的依赖关系。
应用实例: 1、去肯德基,汉堡、可乐、薯条、炸鸡翅等是不变的,而其组合是经常变化的,生成出所谓的"套餐"。 2、JAVA 中的 StringBuilder。
优点: 1、建造者独立,易扩展。 2、便于控制细节风险。
缺点: 1、产品必须有共同点,范围有限制。 2、如内部变化复杂,会有很多的建造类。
使用场景: 1、需要生成的对象具有复杂的内部结构。 2、需要生成的对象内部属性本身相互依赖。
注意事项:与工厂模式的区别是:建造者模式更加关注与零件装配的顺序。然后随便举了个例子完事,且不说举的例子是否恰当,能让人看懂,光是上面啰里巴嗦的一段话就让人头大,什么是变与不变?什么叫基本部件不会变,组合经常变?后来想想吧,也可能是自己蠢,反正看完了这种定义,心里有无数个懵逼。用最简单的Person类举例,先复习下它的写法吧:
首先要有这样一个实体类:
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
private double weight;
} 实体类中包含了这个实体的各个属性,比如上面Person类就包含了name, age, height, weight等属性,像android的AlertDialog,可能还会有title, message, PositiveButtonListener, NegativeButtonListener, 这些都是这个实体类的组成部分。
其次要提供一个公共的静态内部类Builder 和 一个私有的构造方法。静态内部类Builder中包含有与这个实体类相同的成员变量,提供私有构造方法的目的是只允许外部通过Builder类来构造这个实体类,不能通过实体类默认的构造函数来构造。
public class Person {
private String mName;
private int mAge;
private double mHeight;
private double mWeight;
private Person(Builder builder) {
this.mName = builder.mName;
this.mAge = builder.mAge;
this.mHeight = builder.mHeight;
this.mWeight = builder.mWeight;
}
public static class Builder {
private String mName;
private int mAge;
private double mHeight;
private double mWeight;
}
}然后要给Builder类添加一个公共的build()方法供别人调用,毕竟你把实体类默认的公共构造方法给写成private的了,总得要给别人再提供一种途径去实体化这个实体类吧。
public class Person {
private String mName;
private int mAge;
private double mHeight;
private double mWeight;
private Person(Builder builder) {
this.mName = builder.mName;
this.mAge = builder.mAge;
this.mHeight = builder.mHeight;
this.mWeight = builder.mWeight;
}
public static class Builder {
private String mName;
private int mAge;
private double mHeight;
private double mWeight;
public Person build() {
return new Person(this);
}
}
}既然选择了使用Builder类来构造未来的实体对象Person,那还需要添加一些具体的setter()方法来帮助构建这个Person, 以前是在Person中写setter()方法,现在既然使用了Builder类来构建,那么这些方法理应移动中Builder中,而且每个setter的东西都是实体类的组成部分,本身并不相关,为了将来能够使用链式编程的写法,在返回时直接返回这个Builder类。
public class Person {
private String mName;
private int mAge;
private double mHeight;
private double mWeight;
private Person(Builder builder) {
this.mName = builder.mName;
this.mAge = builder.mAge;
this.mHeight = builder.mHeight;
this.mWeight = builder.mWeight;
}
public static class Builder {
private String mName;
private int mAge;
private double mHeight;
private double mWeight;
public Builder setName(String name) {
mName = name;
return this;
}
public Builder setAge(int age) {
mAge = age;
return this;
}
public Builder setHeight(double height) {
mHeight = height;
return this;
}
public Builder setWeight(double weight) {
mWeight = weight;
return this;
}
public Person build() {
return new Person(this);
}
}
}这个地方有个小惊喜,我使用android studio 在Builder里创建setter()方法时,居然能自动return this, 只需要选择下拉列表中的“Builder”选项即可,看来Jetbrains的工程师已经考虑到这一点,果然是智能的Java IDE,JB大法好!
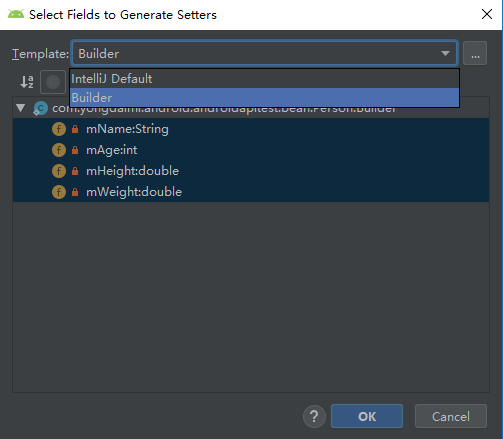
考虑到未来还有可能会读取这个Person类上的成员变量,所以还要给这个Person提供几个getter()方法,方便之后读取。
public class Person {
private String mName;
private int mAge;
private double mHeight;
private double mWeight;
private Person(Builder builder) {
this.mName = builder.mName;
this.mAge = builder.mAge;
this.mHeight = builder.mHeight;
this.mWeight = builder.mWeight;
}
public String getName() {
return mName;
}
public int getAge() {
return mAge;
}
public double getHeight() {
return mHeight;
}
public double getWeight() {
return mWeight;
}
public static class Builder {
private String mName;
private int mAge;
private double mHeight;
private double mWeight;
public Builder setName(String name) {
mName = name;
return this;
}
public Builder setAge(int age) {
mAge = age;
return this;
}
public Builder setHeight(double height) {
mHeight = height;
return this;
}
public Builder setWeight(double weight) {
mWeight = weight;
return this;
}
public Person build() {
return new Person(this);
}
}
}如此这个使用建造者模式的Person类就写好,我们仿照之前调用Android 创建AlertDialog时的链式编程的方式测试一下:
/**
* This Demo is used to demonstrate the use of Builder Pattern
*/
public class BuildPatternApiUseDemoActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
public static final String TAG = "xp.chen";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_build_pattern_api_use_demo);
Person person = new Person.Builder()
.setName("ZhangSan")
.setAge(11)
.setHeight(18.0d)
.setWeight(20.0d)
.build();
Log.i(TAG, "name: "+person.getName()+", age: "+person.getAge()+", height: "+person.getHeight()+", weight: "+person.getWeight());
}
}Log如下:
I/xp.chen: name: ZhangSan, age: 11, height: 18.0, weight: 20.0
以上就是建造者模式的全部创建过程,过程本身并不复杂,麻烦的是不知道什么时候用,胡乱用的话只会适得其反,今天又遇到了一种使用建造者模式的场景,所以结合之前的场景总结下:
一. 作为筛选条件时
经常会在App中看到这样的界面:
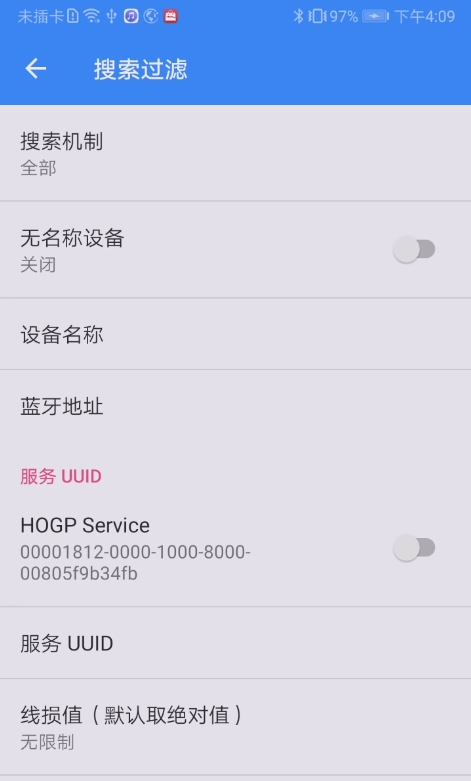
这是一个典型的过滤筛选界面,上面的界面是用于根据各个选项(设备名称、蓝牙地址、服务UUID、线损值)来筛选搜索到的蓝牙列表的。这个时候就很适合使用建造者模式来创建一个筛选类,在筛选类中定义各个筛选条件的成员变量,因为筛选条件的数量是不确定的,比如我只想根据设备名称搜索,我只想根据蓝牙地址搜索,或者我既想根据设备名称又想根据蓝牙地址来搜索,等等, 这个时候就可以通过给Builder设置不同的筛选条件来构造出一个符合预期的筛选对象,然后将筛选对象传过去即可。有个现成的例子就是Android本身定义了这样的一个筛选类,位于:android-sdk\sources\android-28\android\bluetooth\le\ScanFilter.java, 它里面就用到了建造者模式。


/*
* Copyright (C) 2014 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package android.bluetooth.le;
import android.annotation.Nullable;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.ParcelUuid;
import android.os.Parcelable;
import com.android.internal.util.BitUtils;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* Criteria for filtering result from Bluetooth LE scans. A {@link ScanFilter} allows clients to
* restrict scan results to only those that are of interest to them.
* <p>
* Current filtering on the following fields are supported:
* <li>Service UUIDs which identify the bluetooth gatt services running on the device.
* <li>Name of remote Bluetooth LE device.
* <li>Mac address of the remote device.
* <li>Service data which is the data associated with a service.
* <li>Manufacturer specific data which is the data associated with a particular manufacturer.
*
* @see ScanResult
* @see BluetoothLeScanner
*/
public final class ScanFilter implements Parcelable {
@Nullable
private final String mDeviceName;
@Nullable
private final String mDeviceAddress;
@Nullable
private final ParcelUuid mServiceUuid;
@Nullable
private final ParcelUuid mServiceUuidMask;
@Nullable
private final ParcelUuid mServiceDataUuid;
@Nullable
private final byte[] mServiceData;
@Nullable
private final byte[] mServiceDataMask;
private final int mManufacturerId;
@Nullable
private final byte[] mManufacturerData;
@Nullable
private final byte[] mManufacturerDataMask;
/** @hide */
public static final ScanFilter EMPTY = new ScanFilter.Builder().build();
private ScanFilter(String name, String deviceAddress, ParcelUuid uuid,
ParcelUuid uuidMask, ParcelUuid serviceDataUuid,
byte[] serviceData, byte[] serviceDataMask,
int manufacturerId, byte[] manufacturerData, byte[] manufacturerDataMask) {
mDeviceName = name;
mServiceUuid = uuid;
mServiceUuidMask = uuidMask;
mDeviceAddress = deviceAddress;
mServiceDataUuid = serviceDataUuid;
mServiceData = serviceData;
mServiceDataMask = serviceDataMask;
mManufacturerId = manufacturerId;
mManufacturerData = manufacturerData;
mManufacturerDataMask = manufacturerDataMask;
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeInt(mDeviceName == null ? 0 : 1);
if (mDeviceName != null) {
dest.writeString(mDeviceName);
}
dest.writeInt(mDeviceAddress == null ? 0 : 1);
if (mDeviceAddress != null) {
dest.writeString(mDeviceAddress);
}
dest.writeInt(mServiceUuid == null ? 0 : 1);
if (mServiceUuid != null) {
dest.writeParcelable(mServiceUuid, flags);
dest.writeInt(mServiceUuidMask == null ? 0 : 1);
if (mServiceUuidMask != null) {
dest.writeParcelable(mServiceUuidMask, flags);
}
}
dest.writeInt(mServiceDataUuid == null ? 0 : 1);
if (mServiceDataUuid != null) {
dest.writeParcelable(mServiceDataUuid, flags);
dest.writeInt(mServiceData == null ? 0 : 1);
if (mServiceData != null) {
dest.writeInt(mServiceData.length);
dest.writeByteArray(mServiceData);
dest.writeInt(mServiceDataMask == null ? 0 : 1);
if (mServiceDataMask != null) {
dest.writeInt(mServiceDataMask.length);
dest.writeByteArray(mServiceDataMask);
}
}
}
dest.writeInt(mManufacturerId);
dest.writeInt(mManufacturerData == null ? 0 : 1);
if (mManufacturerData != null) {
dest.writeInt(mManufacturerData.length);
dest.writeByteArray(mManufacturerData);
dest.writeInt(mManufacturerDataMask == null ? 0 : 1);
if (mManufacturerDataMask != null) {
dest.writeInt(mManufacturerDataMask.length);
dest.writeByteArray(mManufacturerDataMask);
}
}
}
/**
* A {@link android.os.Parcelable.Creator} to create {@link ScanFilter} from parcel.
*/
public static final Creator<ScanFilter> CREATOR =
new Creator<ScanFilter>() {
@Override
public ScanFilter[] newArray(int size) {
return new ScanFilter[size];
}
@Override
public ScanFilter createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
Builder builder = new Builder();
if (in.readInt() == 1) {
builder.setDeviceName(in.readString());
}
if (in.readInt() == 1) {
builder.setDeviceAddress(in.readString());
}
if (in.readInt() == 1) {
ParcelUuid uuid = in.readParcelable(ParcelUuid.class.getClassLoader());
builder.setServiceUuid(uuid);
if (in.readInt() == 1) {
ParcelUuid uuidMask = in.readParcelable(
ParcelUuid.class.getClassLoader());
builder.setServiceUuid(uuid, uuidMask);
}
}
if (in.readInt() == 1) {
ParcelUuid servcieDataUuid =
in.readParcelable(ParcelUuid.class.getClassLoader());
if (in.readInt() == 1) {
int serviceDataLength = in.readInt();
byte[] serviceData = new byte[serviceDataLength];
in.readByteArray(serviceData);
if (in.readInt() == 0) {
builder.setServiceData(servcieDataUuid, serviceData);
} else {
int serviceDataMaskLength = in.readInt();
byte[] serviceDataMask = new byte[serviceDataMaskLength];
in.readByteArray(serviceDataMask);
builder.setServiceData(
servcieDataUuid, serviceData, serviceDataMask);
}
}
}
int manufacturerId = in.readInt();
if (in.readInt() == 1) {
int manufacturerDataLength = in.readInt();
byte[] manufacturerData = new byte[manufacturerDataLength];
in.readByteArray(manufacturerData);
if (in.readInt() == 0) {
builder.setManufacturerData(manufacturerId, manufacturerData);
} else {
int manufacturerDataMaskLength = in.readInt();
byte[] manufacturerDataMask = new byte[manufacturerDataMaskLength];
in.readByteArray(manufacturerDataMask);
builder.setManufacturerData(manufacturerId, manufacturerData,
manufacturerDataMask);
}
}
return builder.build();
}
};
/**
* Returns the filter set the device name field of Bluetooth advertisement data.
*/
@Nullable
public String getDeviceName() {
return mDeviceName;
}
/**
* Returns the filter set on the service uuid.
*/
@Nullable
public ParcelUuid getServiceUuid() {
return mServiceUuid;
}
@Nullable
public ParcelUuid getServiceUuidMask() {
return mServiceUuidMask;
}
@Nullable
public String getDeviceAddress() {
return mDeviceAddress;
}
@Nullable
public byte[] getServiceData() {
return mServiceData;
}
@Nullable
public byte[] getServiceDataMask() {
return mServiceDataMask;
}
@Nullable
public ParcelUuid getServiceDataUuid() {
return mServiceDataUuid;
}
/**
* Returns the manufacturer id. -1 if the manufacturer filter is not set.
*/
public int getManufacturerId() {
return mManufacturerId;
}
@Nullable
public byte[] getManufacturerData() {
return mManufacturerData;
}
@Nullable
public byte[] getManufacturerDataMask() {
return mManufacturerDataMask;
}
/**
* Check if the scan filter matches a {@code scanResult}. A scan result is considered as a match
* if it matches all the field filters.
*/
public boolean matches(ScanResult scanResult) {
if (scanResult == null) {
return false;
}
BluetoothDevice device = scanResult.getDevice();
// Device match.
if (mDeviceAddress != null
&& (device == null || !mDeviceAddress.equals(device.getAddress()))) {
return false;
}
ScanRecord scanRecord = scanResult.getScanRecord();
// Scan record is null but there exist filters on it.
if (scanRecord == null
&& (mDeviceName != null || mServiceUuid != null || mManufacturerData != null
|| mServiceData != null)) {
return false;
}
// Local name match.
if (mDeviceName != null && !mDeviceName.equals(scanRecord.getDeviceName())) {
return false;
}
// UUID match.
if (mServiceUuid != null && !matchesServiceUuids(mServiceUuid, mServiceUuidMask,
scanRecord.getServiceUuids())) {
return false;
}
// Service data match
if (mServiceDataUuid != null) {
if (!matchesPartialData(mServiceData, mServiceDataMask,
scanRecord.getServiceData(mServiceDataUuid))) {
return false;
}
}
// Manufacturer data match.
if (mManufacturerId >= 0) {
if (!matchesPartialData(mManufacturerData, mManufacturerDataMask,
scanRecord.getManufacturerSpecificData(mManufacturerId))) {
return false;
}
}
// All filters match.
return true;
}
/**
* Check if the uuid pattern is contained in a list of parcel uuids.
*
* @hide
*/
public static boolean matchesServiceUuids(ParcelUuid uuid, ParcelUuid parcelUuidMask,
List<ParcelUuid> uuids) {
if (uuid == null) {
return true;
}
if (uuids == null) {
return false;
}
for (ParcelUuid parcelUuid : uuids) {
UUID uuidMask = parcelUuidMask == null ? null : parcelUuidMask.getUuid();
if (matchesServiceUuid(uuid.getUuid(), uuidMask, parcelUuid.getUuid())) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Check if the uuid pattern matches the particular service uuid.
private static boolean matchesServiceUuid(UUID uuid, UUID mask, UUID data) {
return BitUtils.maskedEquals(data, uuid, mask);
}
// Check whether the data pattern matches the parsed data.
private boolean matchesPartialData(byte[] data, byte[] dataMask, byte[] parsedData) {
if (parsedData == null || parsedData.length < data.length) {
return false;
}
if (dataMask == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; ++i) {
if (parsedData[i] != data[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; ++i) {
if ((dataMask[i] & parsedData[i]) != (dataMask[i] & data[i])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BluetoothLeScanFilter [mDeviceName=" + mDeviceName + ", mDeviceAddress="
+ mDeviceAddress
+ ", mUuid=" + mServiceUuid + ", mUuidMask=" + mServiceUuidMask
+ ", mServiceDataUuid=" + Objects.toString(mServiceDataUuid) + ", mServiceData="
+ Arrays.toString(mServiceData) + ", mServiceDataMask="
+ Arrays.toString(mServiceDataMask) + ", mManufacturerId=" + mManufacturerId
+ ", mManufacturerData=" + Arrays.toString(mManufacturerData)
+ ", mManufacturerDataMask=" + Arrays.toString(mManufacturerDataMask) + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(mDeviceName, mDeviceAddress, mManufacturerId,
Arrays.hashCode(mManufacturerData),
Arrays.hashCode(mManufacturerDataMask),
mServiceDataUuid,
Arrays.hashCode(mServiceData),
Arrays.hashCode(mServiceDataMask),
mServiceUuid, mServiceUuidMask);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) {
return false;
}
ScanFilter other = (ScanFilter) obj;
return Objects.equals(mDeviceName, other.mDeviceName)
&& Objects.equals(mDeviceAddress, other.mDeviceAddress)
&& mManufacturerId == other.mManufacturerId
&& Objects.deepEquals(mManufacturerData, other.mManufacturerData)
&& Objects.deepEquals(mManufacturerDataMask, other.mManufacturerDataMask)
&& Objects.equals(mServiceDataUuid, other.mServiceDataUuid)
&& Objects.deepEquals(mServiceData, other.mServiceData)
&& Objects.deepEquals(mServiceDataMask, other.mServiceDataMask)
&& Objects.equals(mServiceUuid, other.mServiceUuid)
&& Objects.equals(mServiceUuidMask, other.mServiceUuidMask);
}
/**
* Checks if the scanfilter is empty
*
* @hide
*/
public boolean isAllFieldsEmpty() {
return EMPTY.equals(this);
}
/**
* Builder class for {@link ScanFilter}.
*/
public static final class Builder {
private String mDeviceName;
private String mDeviceAddress;
private ParcelUuid mServiceUuid;
private ParcelUuid mUuidMask;
private ParcelUuid mServiceDataUuid;
private byte[] mServiceData;
private byte[] mServiceDataMask;
private int mManufacturerId = -1;
private byte[] mManufacturerData;
private byte[] mManufacturerDataMask;
/**
* Set filter on device name.
*/
public Builder setDeviceName(String deviceName) {
mDeviceName = deviceName;
return this;
}
/**
* Set filter on device address.
*
* @param deviceAddress The device Bluetooth address for the filter. It needs to be in the
* format of "01:02:03:AB:CD:EF". The device address can be validated using {@link
* BluetoothAdapter#checkBluetoothAddress}.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If the {@code deviceAddress} is invalid.
*/
public Builder setDeviceAddress(String deviceAddress) {
if (deviceAddress != null && !BluetoothAdapter.checkBluetoothAddress(deviceAddress)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid device address " + deviceAddress);
}
mDeviceAddress = deviceAddress;
return this;
}
/**
* Set filter on service uuid.
*/
public Builder setServiceUuid(ParcelUuid serviceUuid) {
mServiceUuid = serviceUuid;
mUuidMask = null; // clear uuid mask
return this;
}
/**
* Set filter on partial service uuid. The {@code uuidMask} is the bit mask for the
* {@code serviceUuid}. Set any bit in the mask to 1 to indicate a match is needed for the
* bit in {@code serviceUuid}, and 0 to ignore that bit.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If {@code serviceUuid} is {@code null} but {@code
* uuidMask} is not {@code null}.
*/
public Builder setServiceUuid(ParcelUuid serviceUuid, ParcelUuid uuidMask) {
if (mUuidMask != null && mServiceUuid == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("uuid is null while uuidMask is not null!");
}
mServiceUuid = serviceUuid;
mUuidMask = uuidMask;
return this;
}
/**
* Set filtering on service data.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If {@code serviceDataUuid} is null.
*/
public Builder setServiceData(ParcelUuid serviceDataUuid, byte[] serviceData) {
if (serviceDataUuid == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("serviceDataUuid is null");
}
mServiceDataUuid = serviceDataUuid;
mServiceData = serviceData;
mServiceDataMask = null; // clear service data mask
return this;
}
/**
* Set partial filter on service data. For any bit in the mask, set it to 1 if it needs to
* match the one in service data, otherwise set it to 0 to ignore that bit.
* <p>
* The {@code serviceDataMask} must have the same length of the {@code serviceData}.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If {@code serviceDataUuid} is null or {@code
* serviceDataMask} is {@code null} while {@code serviceData} is not or {@code
* serviceDataMask} and {@code serviceData} has different length.
*/
public Builder setServiceData(ParcelUuid serviceDataUuid,
byte[] serviceData, byte[] serviceDataMask) {
if (serviceDataUuid == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("serviceDataUuid is null");
}
if (mServiceDataMask != null) {
if (mServiceData == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"serviceData is null while serviceDataMask is not null");
}
// Since the mServiceDataMask is a bit mask for mServiceData, the lengths of the two
// byte array need to be the same.
if (mServiceData.length != mServiceDataMask.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"size mismatch for service data and service data mask");
}
}
mServiceDataUuid = serviceDataUuid;
mServiceData = serviceData;
mServiceDataMask = serviceDataMask;
return this;
}
/**
* Set filter on on manufacturerData. A negative manufacturerId is considered as invalid id.
* <p>
* Note the first two bytes of the {@code manufacturerData} is the manufacturerId.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If the {@code manufacturerId} is invalid.
*/
public Builder setManufacturerData(int manufacturerId, byte[] manufacturerData) {
if (manufacturerData != null && manufacturerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid manufacture id");
}
mManufacturerId = manufacturerId;
mManufacturerData = manufacturerData;
mManufacturerDataMask = null; // clear manufacturer data mask
return this;
}
/**
* Set filter on partial manufacture data. For any bit in the mask, set it the 1 if it needs
* to match the one in manufacturer data, otherwise set it to 0.
* <p>
* The {@code manufacturerDataMask} must have the same length of {@code manufacturerData}.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If the {@code manufacturerId} is invalid, or {@code
* manufacturerData} is null while {@code manufacturerDataMask} is not, or {@code
* manufacturerData} and {@code manufacturerDataMask} have different length.
*/
public Builder setManufacturerData(int manufacturerId, byte[] manufacturerData,
byte[] manufacturerDataMask) {
if (manufacturerData != null && manufacturerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid manufacture id");
}
if (mManufacturerDataMask != null) {
if (mManufacturerData == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"manufacturerData is null while manufacturerDataMask is not null");
}
// Since the mManufacturerDataMask is a bit mask for mManufacturerData, the lengths
// of the two byte array need to be the same.
if (mManufacturerData.length != mManufacturerDataMask.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"size mismatch for manufacturerData and manufacturerDataMask");
}
}
mManufacturerId = manufacturerId;
mManufacturerData = manufacturerData;
mManufacturerDataMask = manufacturerDataMask;
return this;
}
/**
* Build {@link ScanFilter}.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException If the filter cannot be built.
*/
public ScanFilter build() {
return new ScanFilter(mDeviceName, mDeviceAddress,
mServiceUuid, mUuidMask,
mServiceDataUuid, mServiceData, mServiceDataMask,
mManufacturerId, mManufacturerData, mManufacturerDataMask);
}
}
}ScanFilter.java
二. 作为配置文件时
这样说的话比较抽象,还是看几个例子吧,比如之前经常使用的图片加载框架UniversalImageLoader,或者是现在大热的Glide 它们本身就包含了几个模块(磁盘缓存大小、下载时线程池的核心线程数大小、图片的缓存路径、默认的解码方式、内存的缓存策略....),这些东西本身就因人而异,要按实际情况去配置,而且每个人的偏好又不同,手机的物理环境也不同,所以使用建造者模式来构造这样一个配置类时,极大的增加了程序的灵活性,每个人都可以视自己的实际情况去配置和更改,使用起来更加舒服。


/**
* Init UIL
*/
private void initImageLoader() {
photoCacheDir = new File(SystemUtil.getCacheDir(), "BreezeResources");
int cacheSize = SystemUtil.getAppMaxRunningMemory() / 5; // set Image Cache Pool Size, Now I set it is 5;
ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration = new ImageLoaderConfiguration.Builder(
getApplicationContext())
// set memory cache strategy
.memoryCache(new LruMemoryCache(cacheSize))
.memoryCacheSize(cacheSize)
.memoryCacheSizePercentage(13)
// .memoryCacheExtraOptions(480, 800)
.denyCacheImageMultipleSizesInMemory()
// default = device screen dimensions
.taskExecutor(null)
.taskExecutorForCachedImages(null)
// set ThreadPool nums
.threadPoolSize(8)
// set Thread priority
.threadPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY - 1)
.tasksProcessingOrder(QueueProcessingType.FIFO)
// set disk cache strategy
// .diskCacheExtraOptions(480, 800, null)
.diskCacheSize(50 * 1024 * 1024)
.diskCacheFileCount(100000)
// .diskCacheFileNameGenerator(new Md5FileNameGenerator())
.diskCache(new UnlimitedDiskCache(photoCacheDir, null, new BaseFileNameGenerator()))
.imageDownloader(new BaseImageDownloader(getApplicationContext()))
.imageDecoder(new BaseImageDecoder(true))
.defaultDisplayImageOptions(DisplayImageOptions.createSimple())
// .writeDebugLogs() // set is logcat debug info
.build();
ImageLoader.getInstance().init(configuration);
}配置UniversalImageLoader的相关属性
又比如之前做的FFmpeg播放器,一个Player需要有解封装器、视频解码器、音频解码器、硬件解码器、OpenGL ES 渲染、libYUV 等等这些东西,我们可以做成建造者模式,在配置时指定哪些Feature开启,或者是使用哪些Feature, 这样通过一个配置类,播放器就能够及时的调整内部的功能模块,创建出一个符合要求的播放器。
三. 单纯的构造出一个东西
这种情况其实和上面的两种情况有些重复,最典型的莫过于android的AlertDialog了,AlertDialog本身具有title , message , contentView这些属性,这些属性不是全部必须的,比如你不设置title那显示出来的Dialog就没有title,你不更改Dialog上左右两个按钮的文字,那它显示时就显示默认文字,所以通过建造者模式,你可以构建出各种各样不同的Dialog, 这也算是建造者模式的应用场景之一吧。
参考链接:
1. Android中所涉及到设计模式
 IDEA激活码
IDEA激活码


