一、通用
首先讨论在使用以下任何API进行开发时必须考虑的一些一般性问题。除了这里引出的问题外,编程者还必须注意他想要使用的网络协议的特殊性。如果没有注意到这种特殊性,例如交换信息的正确顺序,就不能确保我们能够与另一个主机通信。
1.1 字节顺序
在网络通信中,字节顺序(也称为endianness)对于正确设置和解释字段至关重要。每当一个值需要超过1字节的存储空间时,我们就必须在网络字节顺序和主机字节顺序之间进行转换。根据所使用的协议和操作系统,网络字节顺序和主机字节顺序可能不同。对于IP协议,网络字节顺序是大端编址,因此每当主机的字节顺序不是大端编址时,我们就必须进行转换[5]。
对于用于IP协议的转换,Berkeley套接字API提供了一组标准函数,这些函数在头文件<arpa/inet.h>:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| uint32_t htonl(uint32_t hostlong) | host-to-network |
| uint16_t htons(uint16_t hostshort) | host-to-network |
| uint32_t ntohl(uint32_t netlong) | network-to-host |
| uint16_t ntohs(uint16_t netshort) | network-to-host |
Linux环境下通过套接字接收/发送的数据总是按网络字节顺序[5]。
1.2 checksum
许多用于网络通信的协议使用校验和来检测传输错误。有不同的方法来计算校验和。如果我们选择完全由自己生成首部,我们必须手动计算和设置适用的头字段。如果我们这样做,有几点需要考虑:
- 使用哪种算法来计算校验和
- 首部的哪些字段(有时甚至是多个首部的字段)必须包含在校验和的计算中[5]。当然,用户数据可能也被包含在计算中
- 如果我们想计算校验和,所有的头信息需要已经经过了正确的设置
- 我们是否必须计算校验和,或者可以通过网络驱动程序/硬件(例如以太网校验和)、操作系统或预定义函数调用自动计算校验和[5]。
作为计算校验和的一个可能的代码示例,附录中给出了用于计算因特网校验和的listling,这个listing随RFC 1071一起提供的。
1.3 Type-Casting
C语言的一个基本功能是支持类型转换。将二进制数据转换为C中的数据结构的能力对于程序员更容易地处理头数据是至关重要的。要执行类型转换,只需创建指向所需结构的指针:
struct header* protocolHeader;
Then we do need a pointer to the memory space where the binary data of the packet is stored, in our examples mostly a char-Array with a fixed SIZE[5]:
char buffer[SIZE];
Finally we can cast the binary data to our struct and afterwards are able to access the header fields[5]:
protocolHeader = (struct header*) buffer;
在访问header字段时,我们仍然需要处理前面提到的字节顺序。对于大多数众所周知的协议,库中包含的头文件中都有预定义的结构。下表显示了一些可用的头,但它只显示了可用头结构的一部分。根据操作系统和库的不同,可能会提供更多的头文件:
| Header-File | Description |
|---|---|
| <netinet/ip.h> | Defines macros, variables, and structures for IP. |
| <netinet/ip_icmp.h> | Defines macros, variables, and structures for ICMP. |
| <netinet/udp.h> | Defines macros, variables, and structures for UDP. |
| <netinet/tcp.h> | Defines macros, variables, and structures for TCP |
| <netns/idp.h> | Defines IPX packet headers. |
| <netns/sp.h> | Defines SPX packet header. |
| <ssl.h> | Defines SSL prototypes, macros, variables, and structures. |
1.4 Header-Positions
另一个必须考虑的问题是首部在二进制数据中的位置。必须考虑以下因素:
- 较低层的头总是封装较高层的头和数据
- 最低层的首部总是可以在二进制数据包的开头找到。可能不是所有字段都存在,例如数据链路层中的以太网协议就是这种情况。对于以太网协议,前导码、帧起始分隔符和帧校验和由网络驱动程序删除,因为它们更属于物理层(OSI层1)[5]。
- 如果我们将二进制数据类型转化为结构体,我们必须将最后一个头的长度添加到数据指针中,以获得下一个头的开始[5]
`next_header = (struct header*) (buffer + sizeof(struct header)); - 如果最后一个报头具有可变长度和可选字段(例如IP报头或TCP报头),则要找到正确的起始位置可能比上面所示的简单加操作要困难一些。在这种情况下,我们必须首先得到报头的固定部分,然后访问长度字段,最后计算可选报头的长度。只有这样做之后,我们才能找到下一个首部的开始。如果我们对可选字段的内容感兴趣,我们还必须访问包含可选字段类型的标题字段,并相应地将其转换为正确的类型。
二、RAW-sockets
RAW-socket允许访问传输层(OSI第4层)和网络层(OSI第3层)[5]。它的使用仅限于有效用户ID为0或具有CAP_NET_RAW功能的进程,因为它需要root访问权限[1]。
2.1 socket()
对RAW-socket的读写都需要首先创建套接字。创建套接字使用与普通套接字相同的函数。可在<netinet/in.h>中找到,其形式如下[8]
int socket(int family, int type, int protocol)
其中参数如下:
family
family是一个描述所用地址族的常量值,常量在<sys/socket.h>中进行了定义:
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| AF_LOCAL | Local communication |
| AF_UNIX | Unix domain sockets |
| AF_INET | IP version 4 |
| AF_INET6 | IP version 6 |
| AF_IPX | Novell IPX |
| AF_NETLINK | Kernel user interface device |
| AF_X25 | Reserved for X.25 project |
| AF_AX25 | Amateur Radio AX.25 |
| AF_APPLETALK | Appletalk DDP |
| AF_PACKET | Low level packet interface |
| AF_ALG | Interface to kernel crypto API |
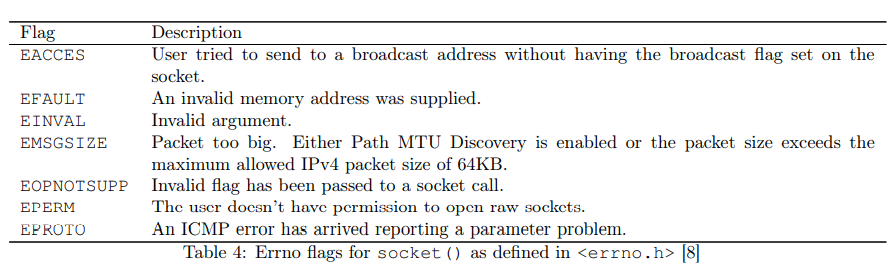
该函数仅在套接字已经建立连接后将源自网络的错误传递给用户。在这种情况下,只传递EMSGSIZE和EPROTO以实现兼容性。如果启用了IP_RECVERR标志位,则所有网络错误都将保存在错误队列中。如果套接字创建成功,则返回非负的套接字描述符;如果在创建套接字期间发生错误,则返回-1。此外<errno.h>中定义的变量errno可以具有以下值[8]:
使用者必须意识到,设置family会影响以后可以选择哪个协议。与RAW-socket一起使用的通常选项是用于发送和接收IPv4数据包的AF_INET。
type
type定义了套接字类型,如下的值在<sys/socket.h>中进行了定义:
| 常量 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SOCK_STREAM | Stream (connection) socket(TCP) |
| SOCK_DGRAM | Datagram (connection-less) socket(UDP) |
| SOCK_RAW | RAW socket |
| SOCK_RDM | Reliably-delivered message |
| SOCK_SEQPACKET | Sequential packet socket |
| SOCK_PACKET | Linux specific way of getting packets at the dev level. |

protocol
protocol定义了套接字发送和接收数据包所使用的协议[8]。协议编号由IANA(互联网分配编号管理局)定义,完整列表可在其网站上找到。<netinet/in.h>中定义了一些协议常量:
| 常量 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| IPPROTO_IP | Dummy protocol. |
| IPPROTO_HOPOPTS | IPv6 Hop-by-Hop options. |
| IPPROTO_ICMP | Internet Control Message Protocol. |
| IPPROTO_IGMP | Internet Group Management Protocol. |
| IPPROTO_IPIP | IPIP tunnels (older KA9Q tunnels use 94). |
| IPPROTO_TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| IPPROTO_EGP | Exterior Gateway Protocol. |
| IPPROTO_PUP | PUP protocol. |
| IPPROTO_UDP | User Datagram Protocol. |
| IPPROTO_IDP | XNS IDP protocol. |
| IPPROTO_TP | SO Transport Protocol Class 4. |
| IPPROTO_IPV6 | IPv6 header. |
| IPPROTO_ROUTING | IPv6 routing header. |
| IPPROTO_FRAGMENT | IPv6 fragmentation header. |
| IPPROTO_RSVP | Reservation Protocol. |
| IPPROTO_GRE | General Routing Encapsulation. |
| IPPROTO_ESP | Encapsulating security payload. |
| IPPROTO_AH | Authentication header. |
| IPPROTO_ICMPV6 | ICMPv6. |
| IPPROTO_NONE | IPv6 no next header. |
| IPPROTO_DSTOPTS | IPv6 destination options. |
| IPPROTO_MTP | Multicast Transport Protocol. |
| IPPROTO_ENCAP | Encapsulation Header. |
| IPPROTO_PIM | Protocol Independent Multicast. |
| IPPROTO_COMP | Compression Header Protocol. |
| IPPROTO_SCTP | Stream Control Transmission Protocol. |
| IPPROTO_RAW | Raw IP packets. |
| IPPROTO_MAX | No description. |
这里protocol的选择受到第一个选项family的影响,只有该family的协议可以选择为protocol。因此,如果选择了我们AF_INET选项,我们只能使用基于IP的协议[8]。
此外,这里应该注意到,大多数操作系统(取决于Linux/Unix发行版)的IPPROTO_RAW意味着套接字还希望用户手动创建IP首部[8]。如果我们选择这个常数,我们就有第3层写入权限。通常的方法是使用另一个常量,然后使用setsockopt()更改套接字选项
In addition to these constants we could also use constants that are defined for layer 2 (PACKET-sockets) to access their protocol information. These constants are operating system dependent and therefore code that uses them cannot be ported as easy as the general constants from the previous table. As an example, table 48 in the appendix shows the constants in Linux for Ethernet protocols which are defined in the <linux/if_ether.h> header.
2.2 setsockopt()
setsockopt()函数可用于更改套接字的options。在不同网络层次军存在options(例如TCP、IP),they are always present at the uppermost socket level.。函数体在<sys/socket.h>头中定义,如下所示:
int setsockopt(int sockfd, int level, int optname, const void * optval, socklen_t optlen)
其中可以设置如下的参数:
- sockfd - 指定需要设定哪个socket的选项
- level - The protocol level of the option we want to set.
- optname - 我们想要设定的选项名,它与optval和optlen一起被未经解释地传递给协议模块进行处理
- optval - 我们要设置的选项值所在的缓冲区,通常是一个整数。It should then be non-zero to enable a Boolean option and zero to disable it.
- optlen - 用字节衡量的optval的缓冲区长度
当修改socket option时,option所在的网络层次及option名需要进行指定。当修改socket API层次的option时,level需要被被设定为SOL_SOCKET。当修改在其他任意层次的option时,the protocol number of the appropriate protocol controlling the option is supplied.例如,为了指明某一个option是被TCP协议使用的,level需要被设定为TCP 的protocol number。
对于以IPPROTO_IP作为参数指定的level,下表显示了<netinet/IP.h>头文件支持并已包含的以下optname:
| optname | 描述 |
|---|---|
| IP_ADD_MEMBERSHIP | Join a multicast group. Argument is an ip_mreqn structure |
| IP_ADD_SOURCE_MEMBERSHIP | Join a multicast group and allow receiving data only from a specified source |
| IP_BLOCK_SOURCE | Stop receiving multicast data from a specific source in a given group |
| IP_DROP_MEMBERSHIP | Leave a multicast group |
| IP_DROP_SOURCE_MEMBERSHIP | Leave a source-specific group-that |
| IP_FREEBIND | If enabled, this boolean option allows binding to an IP address that is non-local/does not exist |
| IP_HDRINCL | If enabled, the user supplies an IP header in front of the user data. Only valid for SOCK_RAW sockets |
| IP_MSFILTER | This option provides access to the advanced full-state filtering API |
| IP_MTU_DISCOVER | Set or receive the Path MTU Discovery setting for a socket |
| IP_MULTICAST_IF | Set the local device for a multicast socket |
| IP_MULTICAST_LOOP | Set or read an argument that determines if multicast packets should be looped back to the local sockets |
| IP_MULTICAST_TTL | Set or read the time-to-live value of outgoing multicast packets for this socket |
| IP_NODEFRAG | If enabled (nonzero), the reassembly of outgoing packets is disabled in the netfilter layer |
| IP_OPTIONS | Set or get the IP options to be sent with every packet from this socket |
| IP_PKTINFO | Pass an IP_PKTINFO ancillary message that supplies information about the incoming packet |
| IP_RECVERR | Enable extended reliable error message passing. On a datagram socket, all generated errors are stored in a per-socket error queue |
| IP_RECVTOS | If enabled the IP_TOS ancillary message is passed with incoming packets |
| IP_RECVTTL | If set, pass a IP_TTL control message with the received packets TTL. Not supported for SOCK_STREAM sockets |
| IP_RETOPTS | Identical to IP_RECVOPTS, but returns raw unprocessed options with timestamp and route record options not filled in for this hop |
| IP_ROUTER_ALERT | Pass all to-be forwarded packets with the IP Router Alert option set to this socket. Only valid for raw sockets. |
| IP_TOS | Set or get the TOS field that is sent with every IP packet originating from this socket. |
| IP_TRANSPARENT | Setting this boolean option enables transparent proxying on this socket. |
| IP_TTL | Set or get the current time-to-live field that is used in every packet sent from this socket. |
| IP_UNBLOCK_SOURCE | Unblock previously blocked multicast source. |
函数执行成功时返回0,如果发生错误返回-1。
2.3 getsockopt
2.4 bind
在创建了一个socket后,我们就可以将创建的socket和一个特定的address绑定到一起。通常来讲这个过程叫做assigning a name to a socket。对于RAW-socket和PACKET-socket来讲这个过程是可选的,但是我们通常使用它来定义我们包的source address,同时也用它来定义我们想要从哪个network-interface来读取包。其他类型的socket可能要求在使用前绑定到一个特定的address。具体地,我们使用<sys/socket.h>中定义的bind()函数来将socket绑定到一个特定的IP地址。
函数体如下:
int bind(int sockfd,const struct sockaddr * addr, socklen_t addrlen);
其中参数如下:
- sockfd:指定需要设定地址的socket
- addr:需要设定其中地址信息的地址数据结构
- addrlen:地址数据结构的字节大小
当函数成功执行时返回0,执行失败时返回-1。
2.5 getsockname
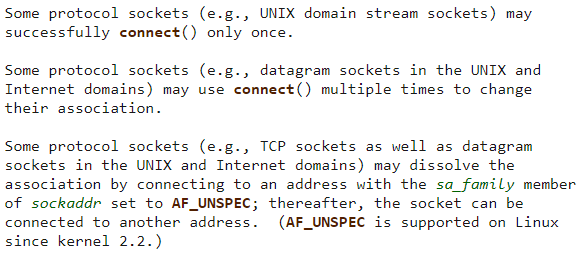
2.6 connect
这个函数用于初始化一个有具体目的地址的连接,write、send、read以及recv函数都需要这个函数。
对于connection based的协议,例如SOCK_STREAM这个函数同样会尝试从另一端建立连接。对于datagram based的协议,only the default destination is defined with this function。函数在<sys/socket.h>中进行了定义,函数体如下:
int connect(int sockfd,const struct sockaddr *addr,socklen_t addrlen);
其中参数如下:
- sockfd:指定进行连接的socket的文件描述符
- addr:sockaddr*结构体指针,指定了连接的另一方
- addrlen:addr的长度
注意如果socket sockfd是SOCK_DGRAM类型,那么addr是datagram默认发送的地址,也是接收datagram的唯一地址。如果socket是SOCK_STREAM或SOCK_SEQPACKET类型,那么调用这个函数会尝试和addr指定的地址绑定的socket进行连接。
当函数成功执行时返回0,失败时返回-1。
参考
2.7 read
2.8 write
我们可以用三种不同的方式通过套接字发送数据。write()和send()函数都需要先定义目标地址,这可以通过使用connect()函数实现。sendto()具有定义目标地址的选项,但也可以使用connect()函数设置。对于以上三种方式,我们都必须考虑缓冲区约束,否则在所有数据传输完全之前,写入连接将关闭。
2.8.1 write
2.8.2 send
2.8.3 sendto
sendto()函数允许我们定义一个数据应该发送到的特定地址,而不必首先调用connect()来设置目标地址[8]。需要注意的是,如果在连接模式(connection-mode)套接字上使用sendto()函数,则会忽略额外的地址信息,并在errno中返回EISCONN错误(如果未分别设置为NULL和零)[8]。这是因为对于这样的套接字,连接类型已经指定了目标。要使用此函数,必须包含<sys/types.h>(对于数据类型)和<sys/socket.h>(对于函数)。函数的调用方式如下[8]:
ssize_t sendto(int sockfd, void * buf, size_t len, int flags, struct sockaddr * dest_addr, socklen_t addrlen)
需要设置的参数如下:
- sockfd - 指定我们通过哪个socket将数据发送出去
- buf - 指定了我们想要通过socket发送的二进制数据所在的内存空间
- len - 指定了从给定的内存空间中应当读取多少数据用于传输
- dest_addr - 该函数使用此参数定义一个结构sockaddr*,其中包含套接字地址族和该族的协议地址。参数可以设置为空,这时不填写
- addrlen - 提供给socket的dest_addr的长度
- flags - 可以为这个方程设置的flag如下表所示
| Flag | 描述 |
|---|---|
| MSG_CONFIRM | Only valid on SOCK_DGRAM and SOCK_RAW. Tell the layer 2 that you got a successful reply from the other side |
| MSG_DONTROUTE | Don’t use a gateway to send out the packet, only send to hosts on directly connected networks. |
| MSG_DONTWAIT | Enables non-blocking operation, if the operation would block EAGAIN or EWOULDBLOCK is returned. |
| MSG_EOR | Terminates a record (when this notion is supported). |
| MSG_MORE | The caller has more data to send. This flag is used with UDP/TCP sockets. |
| MSG_NOSIGNAL | Requests not to send SIGPIPE on errors on stream oriented sockets when the other end breaks the connection. The EPIPE error is still returned. |
| MSG_OOB | Sends out-of-band data on sockets that support this notion, the underlying protocol must also support out-of-band data. |
 IDEA激活码
IDEA激活码


