用法
ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); // 无初始值
ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> "123"); // 有初始值
threadLocal.set("123"); // set操作
threadLocal.get(); // get操作
threadLocal.remove(); // remove操作
一个小例子:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadLocal threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal();
threadLocal.set("Hello");
System.out.println("现在线程是" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", 尝试获取:" + threadLocal.get());
new Thread(() -> {
threadLocal.set("World");
System.out.println("现在线程是" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", 尝试获取:" + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.remove();
}).start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("现在线程是" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", 尝试获取:" + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.remove();
}
输出:
现在线程是main, 尝试获取:Hello
现在线程是Thread-0, 尝试获取:World
现在线程是main, 尝试获取:Hello
实现
set操作
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); // 获取ThreadLocalMap
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value); // 创建map
}
// getMap
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
public class Thread implements Runnable {
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
}
// createMap
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY]; // INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); // 计算下标
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY); // 设置阈值
}
// 哈希值
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT); // HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
}
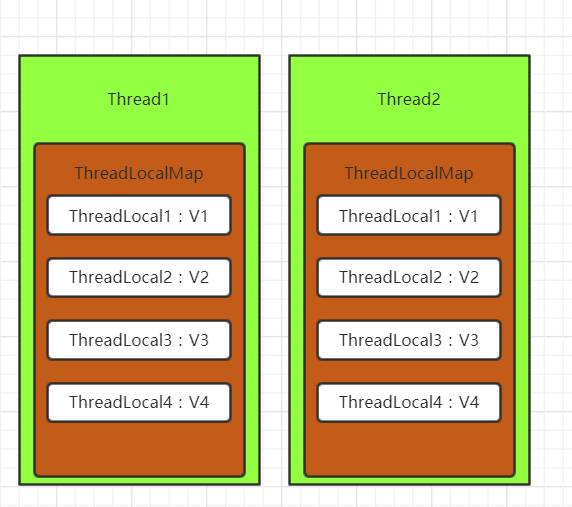
// ThreadLocalMap数据结构
static class ThreadLocalMap {
private Entry[] table;
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
}
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); // 下标
// 使用线性探测法来解决哈希冲突
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); // 获取弱引用ThreadLocal
if (k == key) { // 对于已经存在的key,直接赋值
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) { // 弱引用ThreadLocal为null,进行替换
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); // 上面两种情况不是,直接赋值
int sz = ++size; // size+1
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) // 清除无效entry,大于阈值,扩容并重新散列化
rehash();
}
get操作
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); // 获取ThreadLocalMap
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); // 传入自己,也就是threadlocal对象,得到entry
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1); // 获得下标
Entry e = table[i]; // 取值
if (e != null && e.get() == key) // 正好取到,直接返回
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) { // 依次加一往后取值
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) // 取到返回
return e;
if (k == null) // 弱引用ThreadLocal为null,清除无效的entry
expungeStaleEntry(i); //
else
i = nextIndex(i, len); // 下一个
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
remove操作
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear(); // 弱引用的引用置为null
expungeStaleEntry(i); // 清除entry,并重新散列化
return;
}
}
}
public void clear() {
this.referent = null;
}
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 槽置为null
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// 后面的进行重新散列化
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}
内存泄露
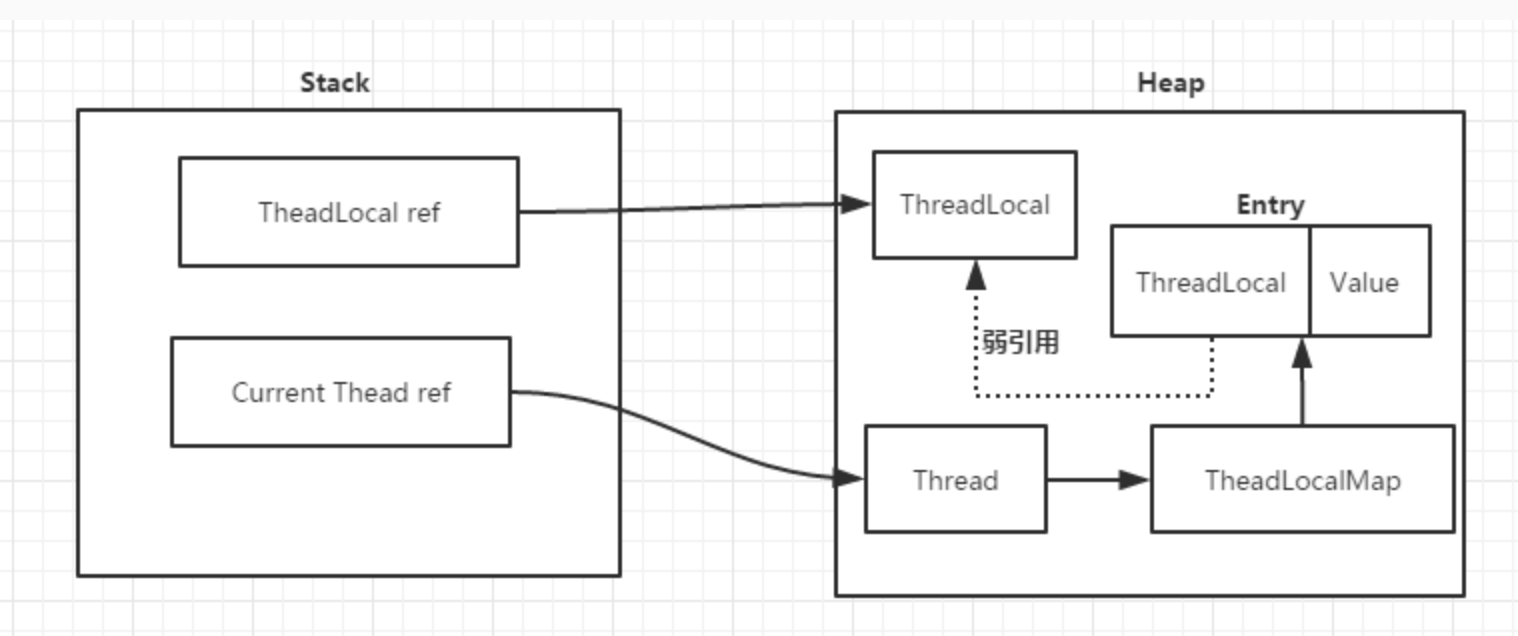
当ThreadLocal没有强依赖,ThreadLocal会在下一次发生GC时被回收,key是被回收了,但是value却没有被回收,为了防止这个问题出现,最好手动调用remove方法。
 IDEA激活码
IDEA激活码


