背景介绍
目前对于一些非核心操作,如增减库存后保存操作日志发送异步消息时(具体业务流程),一旦出现MQ服务异常时,会导致接口响应超时,因此可以考虑对非核心操作引入服务降级、服务隔离。
Hystrix说明
官方文档
Hystrix是Netflix开源的一个容灾框架,解决当外部依赖故障时拖垮业务系统、甚至引起雪崩的问题。
为什么需要Hystrix?
-
在大中型分布式系统中,通常系统很多依赖(HTTP,hession,Netty,Dubbo等),在高并发访问下,这些依赖的稳定性与否对系统的影响非常大,但是依赖有很多不可控问题:如网络连接缓慢,资源繁忙,暂时不可用,服务脱机等。
-
当依赖阻塞时,大多数服务器的线程池就出现阻塞(BLOCK),影响整个线上服务的稳定性,在复杂的分布式架构的应用程序有很多的依赖,都会不可避免地在某些时候失败。高并发的依赖失败时如果没有隔离措施,当前应用服务就有被拖垮的风险。
例如:一个依赖30个SOA服务的系统,每个服务99.99%可用。
99.99%的30次方 ≈ 99.7%
0.3% 意味着一亿次请求 会有 3,000,00次失败
换算成时间大约每月有2个小时服务不稳定.
随着服务依赖数量的变多,服务不稳定的概率会成指数性提高.
解决问题方案:对依赖做隔离。
Hystrix设计理念
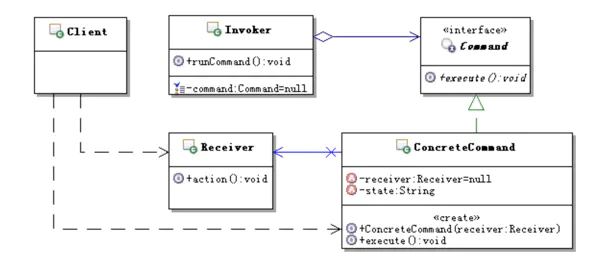
想要知道如何使用,必须先明白其核心设计理念,Hystrix基于命令模式,通过UML图先直观的认识一下这一设计模式。
-
可见,Command是在Receiver和Invoker之间添加的中间层,Command实现了对Receiver的封装。
-
API既可以是Invoker又可以是reciever,通过继承Hystrix核心类HystrixCommand来封装这些API(例如,远程接口调用,数据库查询之类可能会产生延时的操作)。
-
就可以为API提供弹性保护了。
Hystrix如何解决依赖隔离
-
Hystrix使用命令模式HystrixCommand(Command)包装依赖调用逻辑,每个命令在单独线程中/信号授权下执行。
-
可配置依赖调用超时时间,超时时间一般设为比99.5%平均时间略高即可。当调用超时时,直接返回或执行fallback逻辑。
-
为每个依赖提供一个小的线程池(或信号),如果线程池已满调用将被立即拒绝,默认不采用排队,加速失败判定时间。
-
依赖调用结果分,成功,失败(抛出异常),超时,线程拒绝,短路。 请求失败(异常,拒绝,超时,短路)时执行fallback(降级)逻辑。
-
提供熔断器组件,可以自动运行或手动调用,停止当前依赖一段时间(10秒),熔断器默认错误率阈值为50%,超过将自动运行。
-
提供近实时依赖的统计和监控
Hystrix流程结构解析
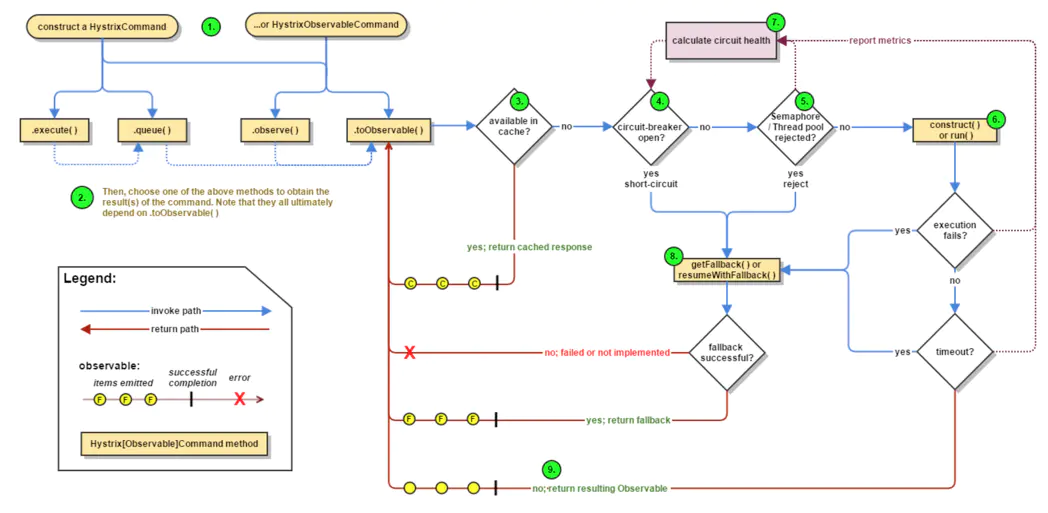
、
流程说明:
-
每次调用构建HystrixCommand或者HystrixObservableCommand对象,把依赖调用封装在run()方法中.
-
结果是否有缓存如果没有执行execute()/queue做sync或async调用,对应真正的run()/construct()
-
判断熔断器(circuit-breaker)是否打开,如果打开跳到步骤8,进行降级策略,如果关闭进入步骤.
-
判断线程池/队列/信号量是否跑满,如果跑满进入降级步骤8,否则继续后续步骤.
-
使用HystrixObservableCommand.construct()还是HystrixCommand.run(),运行依赖逻辑
-
依赖逻辑调用超时,进入步骤8
-
判断逻辑是否调用成功
-
6a 返回成功调用结果
-
6b 调用出错,进入步骤8.
-
-
计算熔断器状态,所有的运行状态(成功, 失败, 拒绝,超时)上报给熔断器,用于统计从而判断熔断器状态.
-
getFallback()降级逻辑.
a. 没有实现getFallback的Command将直接抛出异常b. fallback降级逻辑调用成功直接返回
c. 降级逻辑调用失败抛出异常
-
返回执行成功结果
以下四种情况将触发getFallback调用:
-
run()方法抛出非HystrixBadRequestException异常。
-
run()方法调用超时
-
熔断器开启短路调用
-
线程池/队列/信号量是否跑满
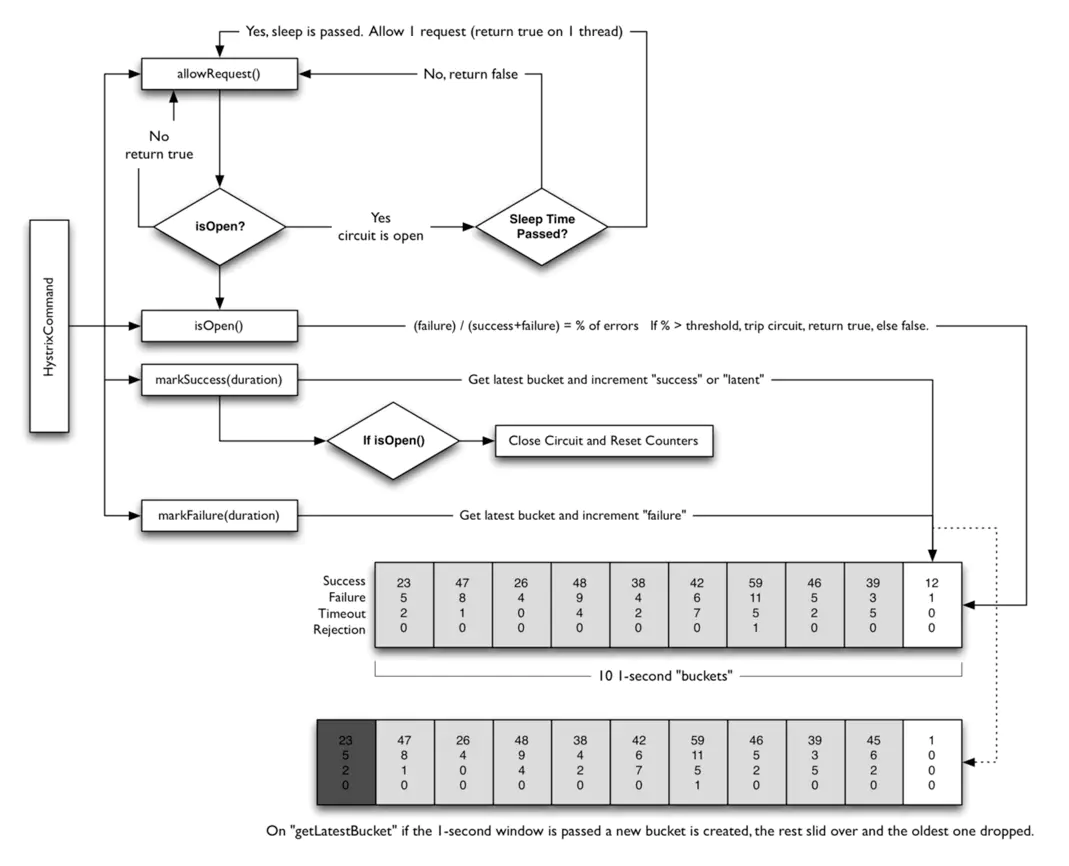
熔断器:Circuit Breaker
每个熔断器默认维护10个bucket,每秒一个bucket,每个bucket记录成功,失败,超时,拒绝的状态,默认错误超过50%且10秒内超过20个请求进行中断短路。
Hystrix隔离分析
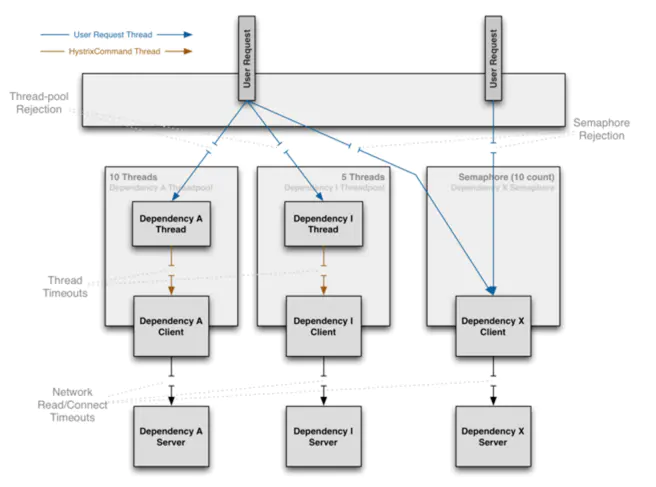
Hystrix隔离方式采用线程/信号的方式,通过隔离限制依赖的并发量和阻塞扩散.
线程隔离
-
执行依赖代码的线程与请求线程(如:jetty线程)分离,请求线程可以自由控制离开的时间(异步过程)。
-
通过线程池大小可以控制并发量,当线程池饱和时可以提前拒绝服务,防止依赖问题扩散。
-
线上建议线程池不要设置过大,否则大量堵塞线程有可能会拖慢服务器。
实际案例:
Netflix公司内部认为线程隔离开销足够小,不会造成重大的成本或性能的影响。Netflix 内部API 每天100亿的HystrixCommand依赖请求使用线程隔,每个应用大约40多个线程池,每个线程池大约5-20个线程。
信号隔离
信号隔离也可以用于限制并发访问,防止阻塞扩散, 与线程隔离最大不同在于执行依赖代码的线程依然是请求线程(该线程需要通过信号申请),如果客户端是可信的且可以快速返回,可以使用信号隔离替换线程隔离,降低开销。
信号量的大小可以动态调整, 线程池大小不可以。
线程隔离与信号隔离区别如下图:
fallback故障切换降级机制
有兴趣的小伙伴可以看看:官方参考文档
源码分析
hystrix-core-1.5.12-sources.jar!/com/netflix/hystrix/AbstractCommand.java
executeCommandAndObserve
/**
* This decorates "Hystrix" functionality around the run() Observable.
* @return R
*/
private Observable<R> executeCommandAndObserve(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
//......
final Func1<Throwable, Observable<R>> handleFallback = new Func1<Throwable,
Observable<R>>() {
@Override
public Observable<R> call(Throwable t) {
circuitBreaker.markNonSuccess();
Exception e = getExceptionFromThrowable(t);
executionResult = executionResult.setExecutionException(e);
if (e instanceof RejectedExecutionException) {
return handleThreadPoolRejectionViaFallback(e);
} else if (t instanceof HystrixTimeoutException) {
return handleTimeoutViaFallback();
} else if (t instanceof HystrixBadRequestException) {
return handleBadRequestByEmittingError(e);
} else {
/*
* Treat HystrixBadRequestException from ExecutionHook like a plain
* HystrixBadRequestException.
*/
if (e instanceof HystrixBadRequestException) {
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.BAD_REQUEST, commandKey);
return Observable.error(e);
}
return handleFailureViaFallback(e);
}
}
};
//......
Observable<R> execution;
if (properties.executionTimeoutEnabled().get()) {
execution = executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(_cmd).lift(new HystrixObservableTimeoutOperator<R>(_cmd));
} else {
execution = executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(_cmd);
}
return execution.doOnNext(markEmits)
.doOnCompleted(markOnCompleted)
.onErrorResumeNext(handleFallback)
.doOnEach(setRequestContext);
}
使用Observable的onErrorResumeNext,里头调用了handleFallback,handleFallback中区分不同的异常来调用不同的fallback。
-
RejectedExecutionException调用handleThreadPoolRejectionViaFallback
-
HystrixTimeoutException调用handleTimeoutViaFallback
-
非HystrixBadRequestException的调用handleFailureViaFallback
applyHystrixSemantics
private Observable<R> applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
// mark that we're starting execution on the ExecutionHook
// if this hook throws an exception, then a fast-fail occurs with no fallback. No state is left inconsistent
executionHook.onStart(_cmd);
/* determine if we're allowed to execute */
if (circuitBreaker.attemptExecution()) {
final TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore = getExecutionSemaphore();
final AtomicBoolean semaphoreHasBeenReleased = new AtomicBoolean(false);
final Action0 singleSemaphoreRelease = new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
if (semaphoreHasBeenReleased.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
executionSemaphore.release();
}
}
};
final Action1<Throwable> markExceptionThrown = new Action1<Throwable>() {
@Override
public void call(Throwable t) {
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.EXCEPTION_THROWN, commandKey);
}
};
if (executionSemaphore.tryAcquire()) {
try {
/* used to track userThreadExecutionTime */
executionResult = executionResult.setInvocationStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
return executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd)
.doOnError(markExceptionThrown)
.doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease)
.doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
} else {
return handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback();
}
} else {
return handleShortCircuitViaFallback();
}
}
-
applyHystrixSemantics方法针对executionSemaphore.tryAcquire()没通过的调用
-
handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback
-
applyHystrixSemantics方法针对circuitBreaker.attemptExecution()没通过的调用handleShortCircuitViaFallback()
ViaFallback方法
private Observable<R> handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback() {
Exception semaphoreRejectionException = new RuntimeException("could not acquire a semaphore for execution");
executionResult = executionResult.setExecutionException(semaphoreRejectionException);
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.SEMAPHORE_REJECTED, commandKey);
logger.debug("HystrixCommand Execution Rejection by Semaphore."); // debug only since we're throwing the exception and someone higher will do something with it
// retrieve a fallback or throw an exception if no fallback available
return getFallbackOrThrowException(this, HystrixEventType.SEMAPHORE_REJECTED, FailureType.REJECTED_SEMAPHORE_EXECUTION,
"could not acquire a semaphore for execution", semaphoreRejectionException);
}
private Observable<R> handleShortCircuitViaFallback() {
// record that we are returning a short-circuited fallback
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.SHORT_CIRCUITED, commandKey);
// short-circuit and go directly to fallback (or throw an exception if no fallback implemented)
Exception shortCircuitException = new RuntimeException("Hystrix circuit short-circuited and is OPEN");
executionResult = executionResult.setExecutionException(shortCircuitException);
try {
return getFallbackOrThrowException(this, HystrixEventType.SHORT_CIRCUITED, FailureType.SHORTCIRCUIT,
"short-circuited", shortCircuitException);
} catch (Exception e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
private Observable<R> handleThreadPoolRejectionViaFallback(Exception underlying) {
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.THREAD_POOL_REJECTED, commandKey);
threadPool.markThreadRejection();
// use a fallback instead (or throw exception if not implemented)
return getFallbackOrThrowException(this, HystrixEventType.THREAD_POOL_REJECTED, FailureType.REJECTED_THREAD_EXECUTION, "could not be queued for execution", underlying);
}
private Observable<R> handleTimeoutViaFallback() {
return getFallbackOrThrowException(this, HystrixEventType.TIMEOUT, FailureType.TIMEOUT, "timed-out", new TimeoutException());
}
private Observable<R> handleFailureViaFallback(Exception underlying) {
/**
* All other error handling
*/
logger.debug("Error executing HystrixCommand.run(). Proceeding to fallback logic ...", underlying);
// report failure
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.FAILURE, commandKey);
// record the exception
executionResult = executionResult.setException(underlying);
return getFallbackOrThrowException(this, HystrixEventType.FAILURE, FailureType.COMMAND_EXCEPTION, "failed", underlying);
}
- handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback、handleShortCircuitViaFallback、handleThreadPoolRejectionViaFallback、handleTimeoutViaFallback、handleFailureViaFallback这几个方法调用了getFallbackOrThrowException
- 其eventType分别是SEMAPHORE_REJECTED、SHORT_CIRCUITED、THREAD_POOL_REJECTED、TIMEOUT、FAILURE
- AbstractCommand.getFallbackOrThrowException
hystrix-core-1.5.12-sources.jar!/com/netflix/hystrix/AbstractCommand.java
/**
* Execute <code>getFallback()</code> within protection of a semaphore that limits number of concurrent executions.
* <p>
* Fallback implementations shouldn't perform anything that can be blocking, but we protect against it anyways in case someone doesn't abide by the contract.
* <p>
* If something in the <code>getFallback()</code> implementation is latent (such as a network call) then the semaphore will cause us to start rejecting requests rather than allowing potentially
* all threads to pile up and block.
*
* @return K
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException
* if getFallback() not implemented
* @throws HystrixRuntimeException
* if getFallback() fails (throws an Exception) or is rejected by the semaphore
*/
private Observable<R> getFallbackOrThrowException(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd, final HystrixEventType eventType, final FailureType failureType, final String message, final Exception originalException) {
final HystrixRequestContext requestContext = HystrixRequestContext.getContextForCurrentThread();
long latency = System.currentTimeMillis() - executionResult.getStartTimestamp();
// record the executionResult
// do this before executing fallback so it can be queried from within getFallback (see See https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/pull/144)
executionResult = executionResult.addEvent((int) latency, eventType);
if (isUnrecoverable(originalException)) {
logger.error("Unrecoverable Error for HystrixCommand so will throw HystrixRuntimeException and not apply fallback. ", originalException);
/* executionHook for all errors */
Exception e = wrapWithOnErrorHook(failureType, originalException);
return Observable.error(new HystrixRuntimeException(failureType, this.getClass(), getLogMessagePrefix() + " " + message + " and encountered unrecoverable error.", e, null));
} else {
if (isRecoverableError(originalException)) {
logger.warn("Recovered from java.lang.Error by serving Hystrix fallback", originalException);
}
if (properties.fallbackEnabled().get()) {
/* fallback behavior is permitted so attempt */
final Action1<Notification<? super R>> setRequestContext = new Action1<Notification<? super R>>() {
@Override
public void call(Notification<? super R> rNotification) {
setRequestContextIfNeeded(requestContext);
}
};
final Action1<R> markFallbackEmit = new Action1<R>() {
@Override
public void call(R r) {
if (shouldOutputOnNextEvents()) {
executionResult = executionResult.addEvent(HystrixEventType.FALLBACK_EMIT);
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.FALLBACK_EMIT, commandKey);
}
}
};
final Action0 markFallbackCompleted = new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
long latency = System.currentTimeMillis() - executionResult.getStartTimestamp();
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.FALLBACK_SUCCESS, commandKey);
executionResult = executionResult.addEvent((int) latency,
HystrixEventType.FALLBACK_SUCCESS);
}
};
final Func1<Throwable, Observable<R>> handleFallbackError = new Func1<Throwable, Observable<R>>() {
@Override
public Observable<R> call(Throwable t) {
/* executionHook for all errors */
Exception e = wrapWithOnErrorHook(failureType, originalException);
Exception fe = getExceptionFromThrowable(t);
long latency = System.currentTimeMillis() - executionResult.getStartTimestamp();
Exception toEmit;
if (fe instanceof UnsupportedOperationException) {
logger.debug("No fallback for HystrixCommand. ", fe); // debug only since we're throwing the exception and someone higher will do something with it
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.FALLBACK_MISSING, commandKey);
executionResult = executionResult.addEvent((int) latency, HystrixEventType.FALLBACK_MISSING);
toEmit = new HystrixRuntimeException(failureType, _cmd.getClass(), getLogMessagePrefix() + " " + message + " and no fallback available.", e, fe);
} else {
logger.debug("HystrixCommand execution " + failureType.name() + " and fallback failed.", fe);
eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.FALLBACK_FAILURE, commandKey);
executionResult = executionResult.addEvent((int) latency, HystrixEventType.FALLBACK_FAILURE);
toEmit = new HystrixRuntimeException(failureType, _cmd.getClass(), getLogMessagePrefix() + " " + message + " and fallback failed.", e, fe);
}
// NOTE: we're suppressing fallback exception here
if (shouldNotBeWrapped(originalException)) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
return Observable.error(toEmit);
}
};
final TryableSemaphore fallbackSemaphore = getFallbackSemaphore();
final AtomicBoolean semaphoreHasBeenReleased = new AtomicBoolean(false);
final Action0 singleSemaphoreRelease = new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
if (semaphoreHasBeenReleased.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
fallbackSemaphore.release();
}
}
};
Observable<R> fallbackExecutionChain;
// acquire a permit
if (fallbackSemaphore.tryAcquire()) {
try {
if (isFallbackUserDefined()) {
executionHook.onFallbackStart(this);
fallbackExecutionChain = getFallbackObservable();
} else {
//same logic as above without the hook invocation
fallbackExecutionChain = getFallbackObservable();
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
//If hook or user-fallback throws, then use that as the result of the fallback lookup
fallbackExecutionChain = Observable.error(ex);
}
return fallbackExecutionChain
.doOnEach(setRequestContext)
.lift(new FallbackHookApplication(_cmd))
.lift(new DeprecatedOnFallbackHookApplication(_cmd))
.doOnNext(markFallbackEmit)
.doOnCompleted(markFallbackCompleted)
.onErrorResumeNext(handleFallbackError)
.doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease)
.doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease);
} else {
return handleFallbackRejectionByEmittingError();
}
} else {
return handleFallbackDisabledByEmittingError(originalException, failureType, message);
}
}
}
- fallbackExecutionChain的onErrorResumeNext,调用了handleFallbackError
- fallbackExecutionChain的doOnCompleted,调用了markFallbackCompleted
- AbstractCommand.getFallbackSemaphore
hystrix-core-1.5.12-sources.jar!/com/netflix/hystrix/AbstractCommand.java
/**
* Get the TryableSemaphore this HystrixCommand should use if a fallback occurs.
*
* @return TryableSemaphore
*/
protected TryableSemaphore getFallbackSemaphore() {
if (fallbackSemaphoreOverride == null) {
TryableSemaphore _s = fallbackSemaphorePerCircuit.get(commandKey.name());
if (_s == null) {
// we didn't find one cache so setup
fallbackSemaphorePerCircuit.putIfAbsent(commandKey.name(), new TryableSemaphoreActual(properties.fallbackIsolationSemaphoreMaxConcurrentRequests()));
// assign whatever got set (this or another thread)
return fallbackSemaphorePerCircuit.get(commandKey.name());
} else {
return _s;
}
} else {
return fallbackSemaphoreOverride;
}
}
针对每个commandKey获取或创建TryableSemaphoreActual
fallback源码分析小结
hystrix的fallback主要分为5种类型:
- SEMAPHORE_REJECTED对应handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback
- SHORT_CIRCUITED对应handleShortCircuitViaFallback
- THREAD_POOL_REJECTED对应handleThreadPoolRejectionViaFallback
- TIMEOUT对应handleTimeoutViaFallback
- FAILURE对应handleFailureViaFallback
- 这几个方法最后都调用了getFallbackOrThrowException方法。
 IDEA激活码
IDEA激活码


