title: dubbo 源码解析1
date: 2020/05/14 10:22
本节内容
先带大家整体的过一遍 Dubbo 服务发布和服务发现以及服务调用的流程,在下节的时候会带大家自己实现一个。
一、xml 配置文件解析
我们先看一下 dubbo 的配置文件
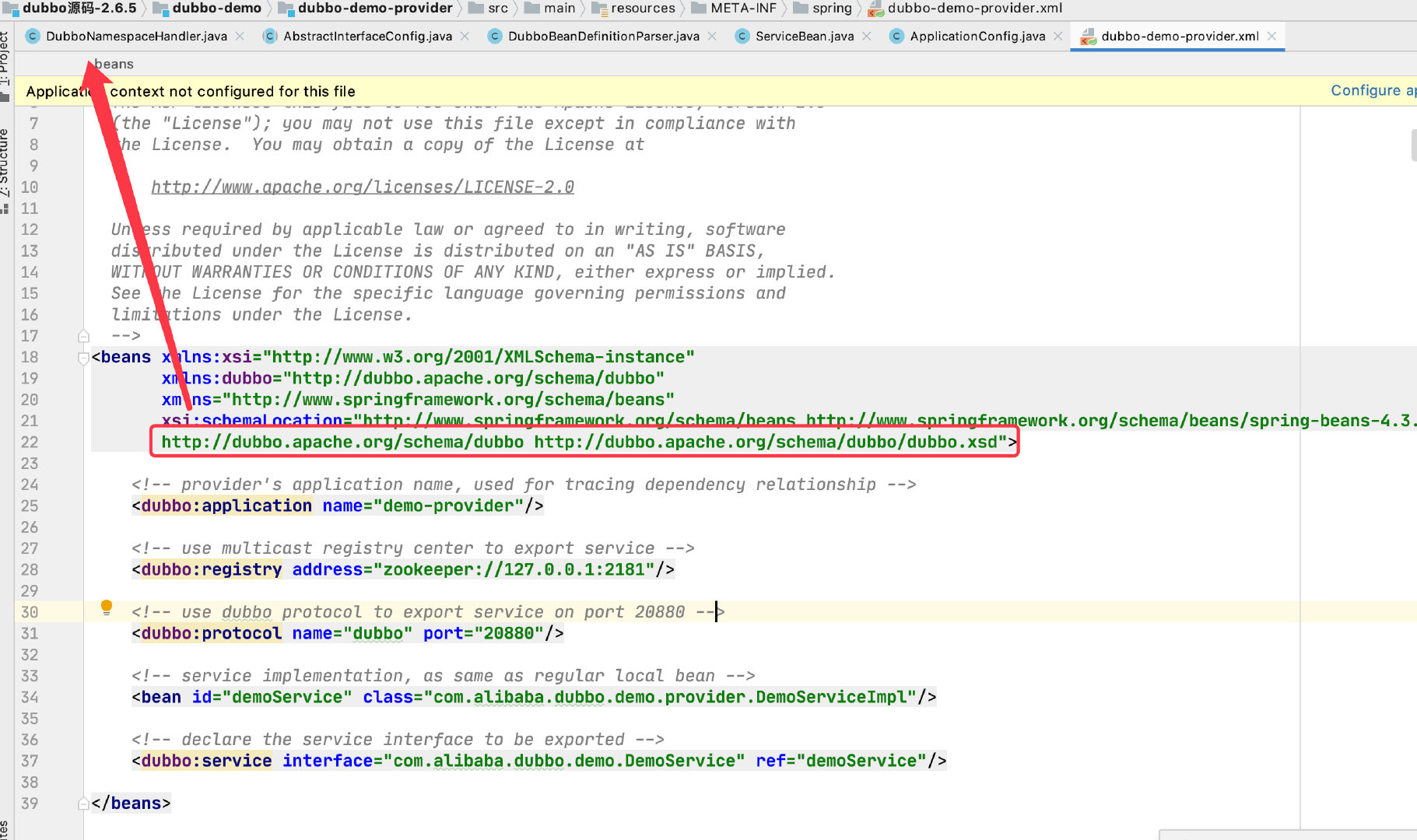
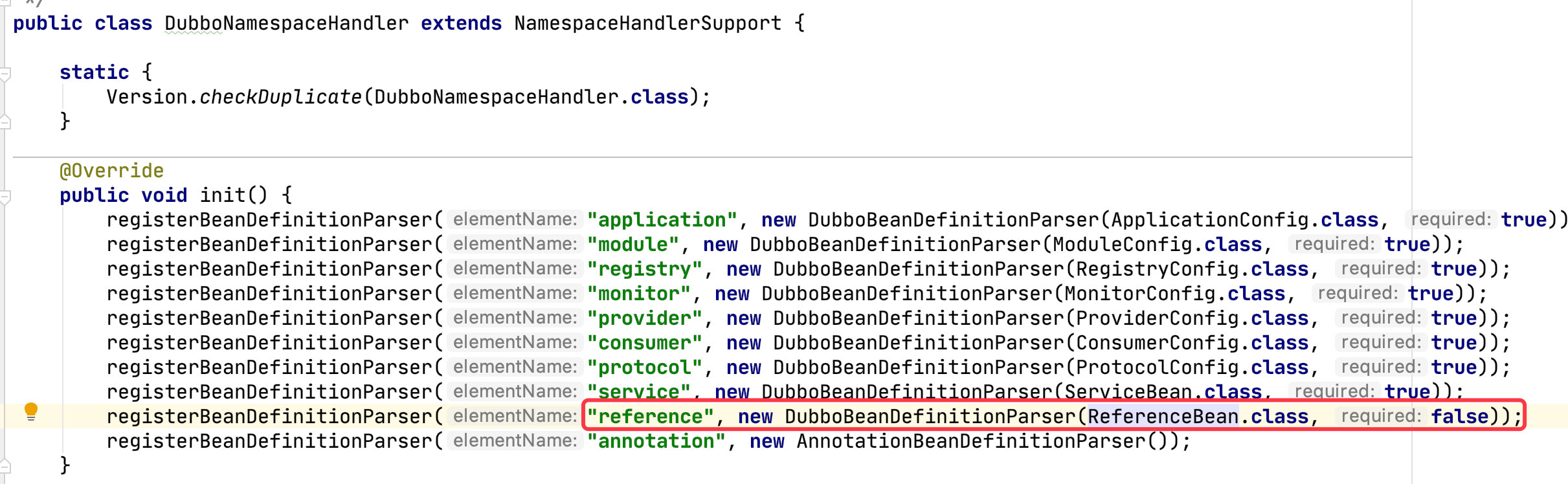
图中框中的这个东西会触发 Spring 的 NamespaceHandlerSupport(我也不知道怎么触发的),然后就调用了 Dubbo 写的 DubboNamespaceHandler
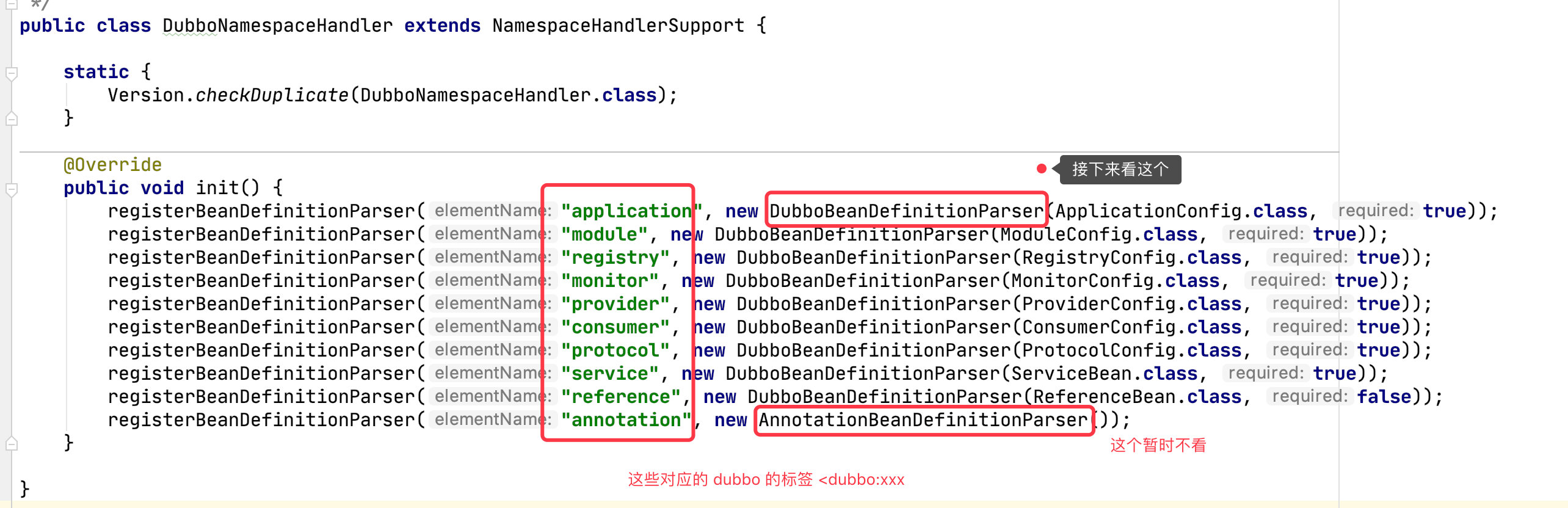
DubboBeanDefinitionParser 就是用来解析标签中的属性的。DubboBeanDefinitionParser 实现了 BeanDefinitionParser, Spring 会调用它的 parse() 方法。
以 ServiceBean 为例,看下 parse 的流程:
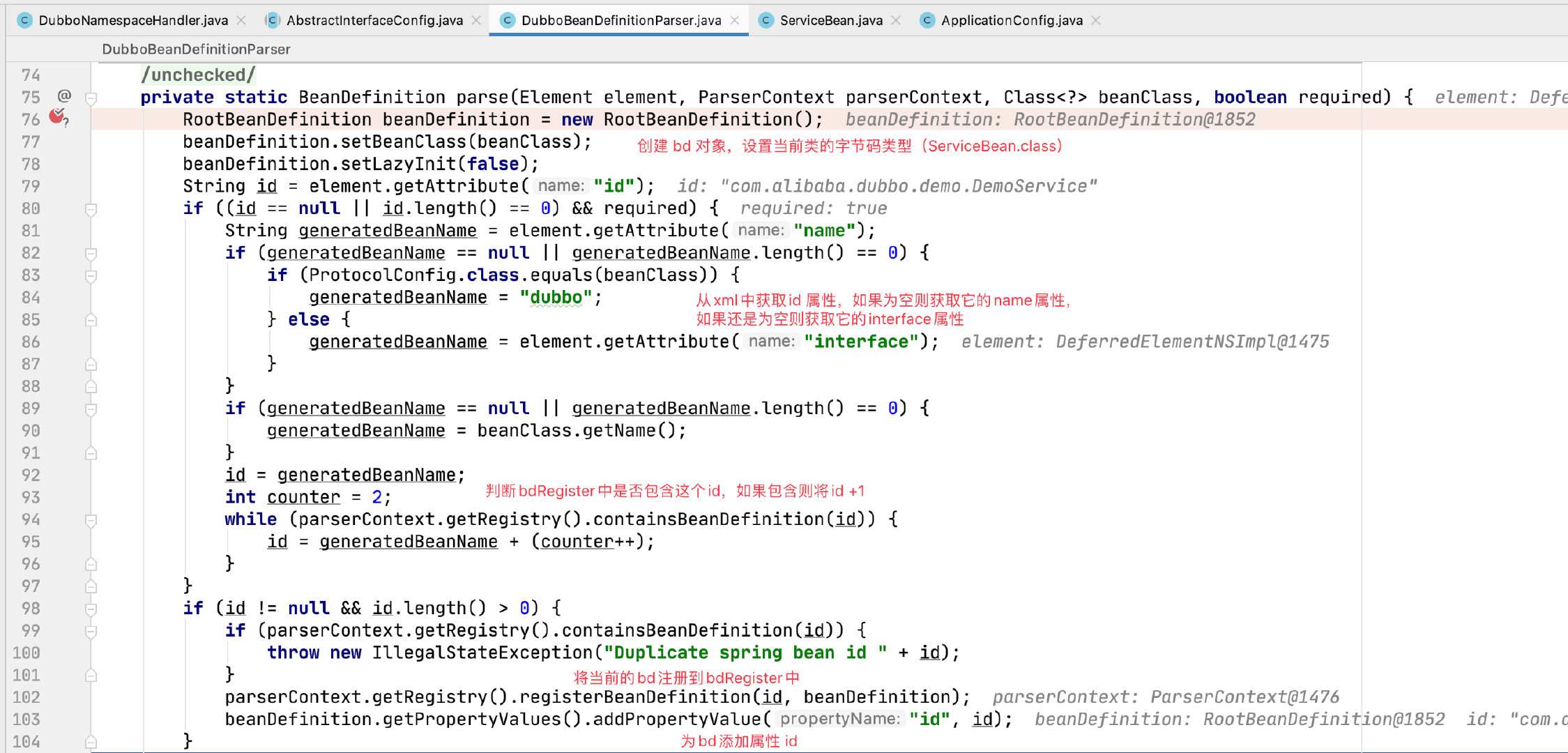
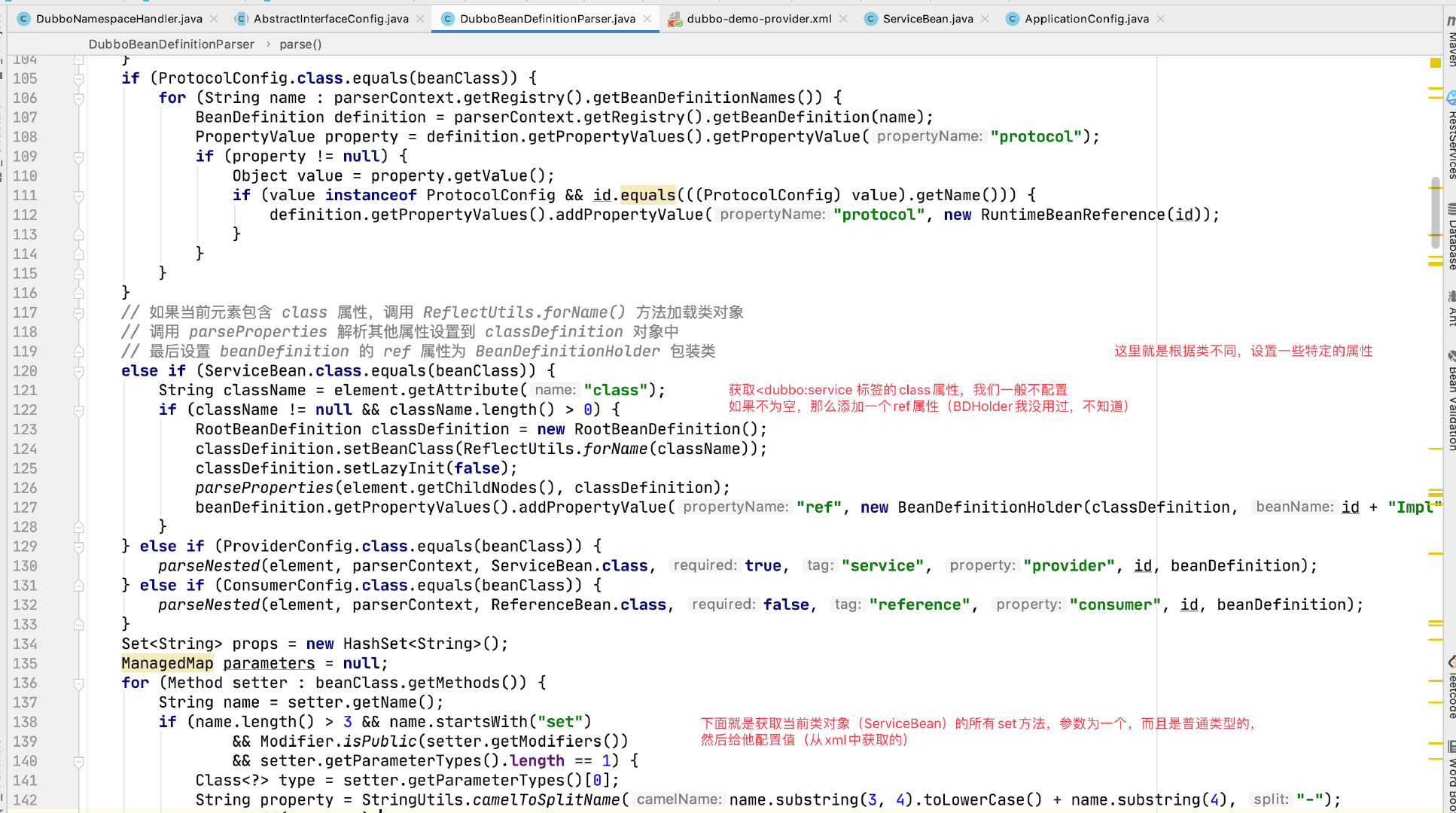
这部分代码就是解析 xml 中配置的那些标签成为对象,然后注册到 Spring 中。
本部分参考
二、服务发布(本地)
我们先看下 ServiceBean 类
public class ServiceBean<T> extends ServiceConfig<T>
implements InitializingBean, // 对象初始化结束时会调用
DisposableBean, // 对象销毁时调用
ApplicationContextAware, // 注入 ApplicationContext 对象
ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>, // 监听器,当容器刷新完毕时会调用
BeanNameAware, // 注入 BeanName
ApplicationEventPublisherAware // 注入事件发布器
InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()

这个方法的作用主要是从容器中取出一些全局的配置,设置到当前对象中。(为啥不用 DI 呢)
ApplicationListener#onApplicationEvent()
doExport() 中大部分代码都是对 ServiceBean 配置校验和初始化代码。大家有兴趣可以自行阅览。这里直接划重点,分析 doExportUrls() 方法。
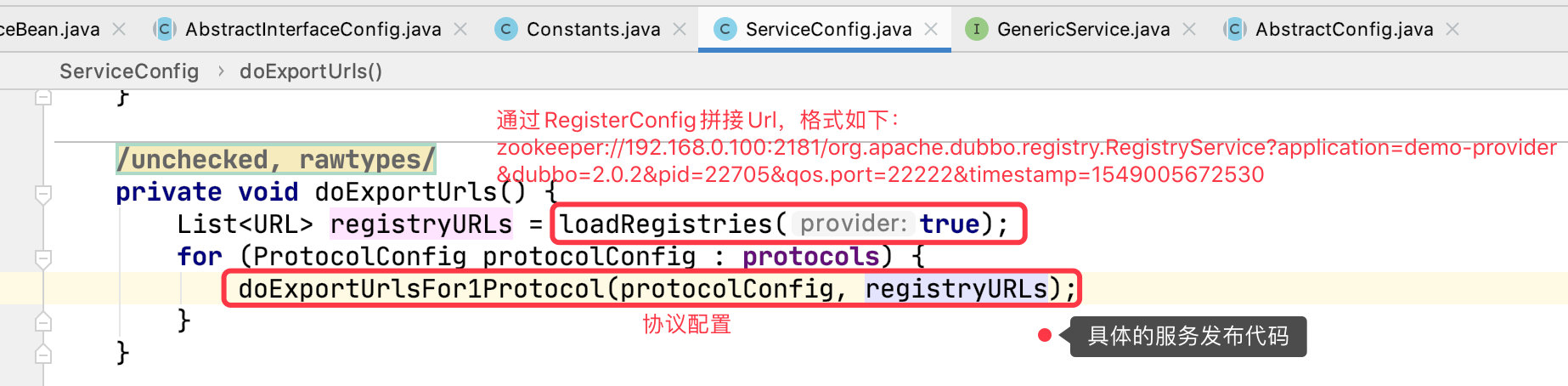
loadRegistries 拼接的是注册中心的地址:
registry://127.0.0.1:2181/com.alibaba.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?
application=demo-provider&dubbo=2.0.2&pid=30841&qos.port=22222®istry=zookeeper×tamp=1589435494957
doExportUrlsFor1Protocol 的前半部分代码拼接的是当前服务对外暴露的地址:
dubbo://192.168.2.94:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demo-provider&bean.name=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&bind.ip=192.168.2.94&bind.port=20880&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=30870&qos.port=22222&side=provider×tamp=1589435771447
将协议改成 injvm
injvm://192.168.2.94:65371/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demo-provider&bean.name=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&bind.ip=192.168.2.94&bind.port=65371&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello¬ify=false&pid=33365&qos.port=22222&side=provider×tamp=1589507274731
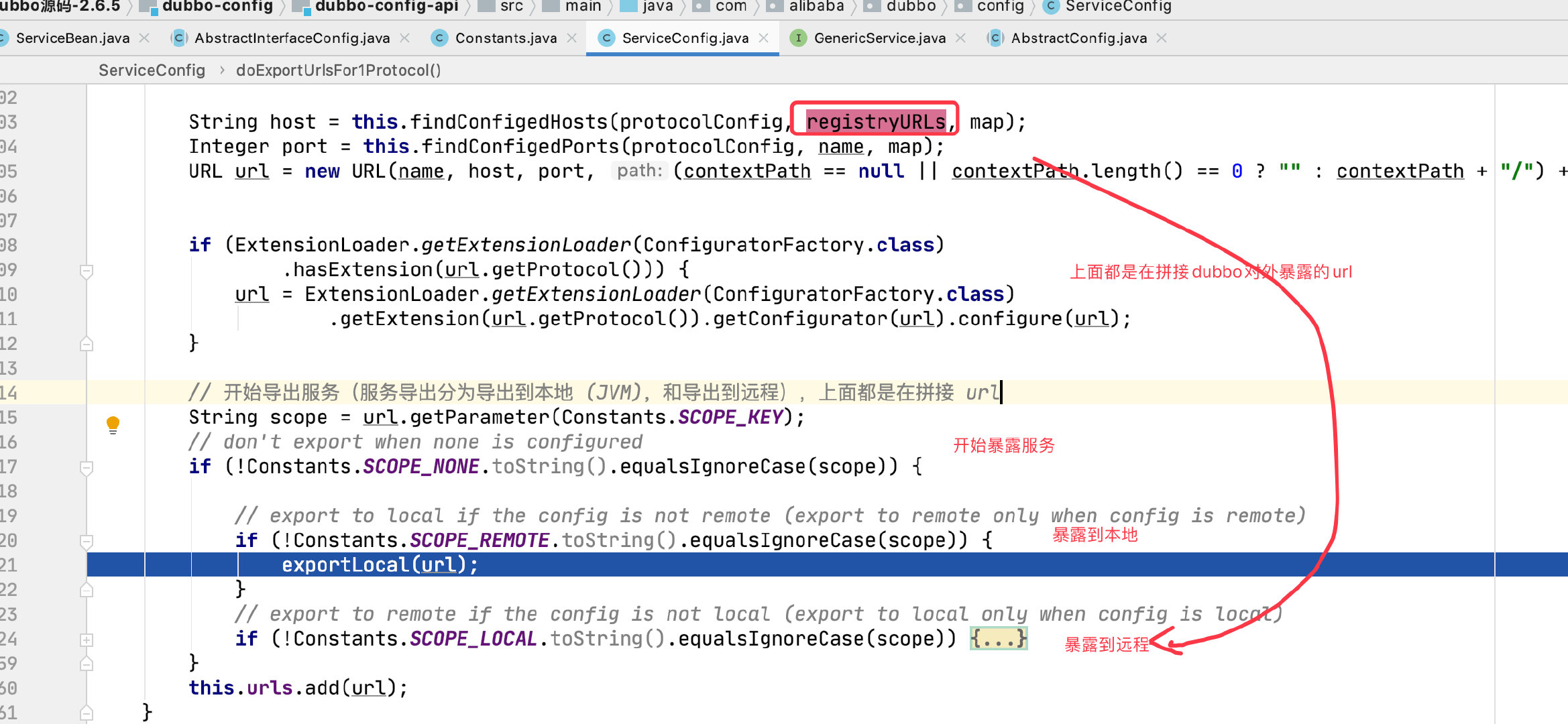
本地暴露(发布)
看 exportLocal() 方法之前先建议读一下SPI自适应扩展

tag1 proxyFactory.getInvoker(ref, (Class) interfaceClass, local)
private static final ProxyFactory proxyFactory = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ProxyFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension(); Dubbo 生成的代理对象
public class ProxyFactory$Adaptive implements org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory {
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker getInvoker(java.lang.Object arg0, java.lang.Class arg1, org.apache.dubbo.common.URL arg2) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg2 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg2;
// 注意这句话,返回的是 javassist
String extName = url.getParameter("proxy", "javassist");
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([proxy])");
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory extension = null;
try {
// 所以这里获取到的是 StubProxyFactoryWrapper 对象
extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory.class).getExtension(extName);
}catch(Exception e){
if (count.incrementAndGet() == 1) {
logger.warn("Failed to find extension named " + extName + " for type org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory, will use default extension javassist instead.", e);
}
extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory.class).getExtension("javassist");
}
// 调用 StubProxyFactoryWrapper 对象的 getInvoker() 方法
return extension.getInvoker(arg0, arg1, arg2);
}
}
StubProxyFactoryWrapper
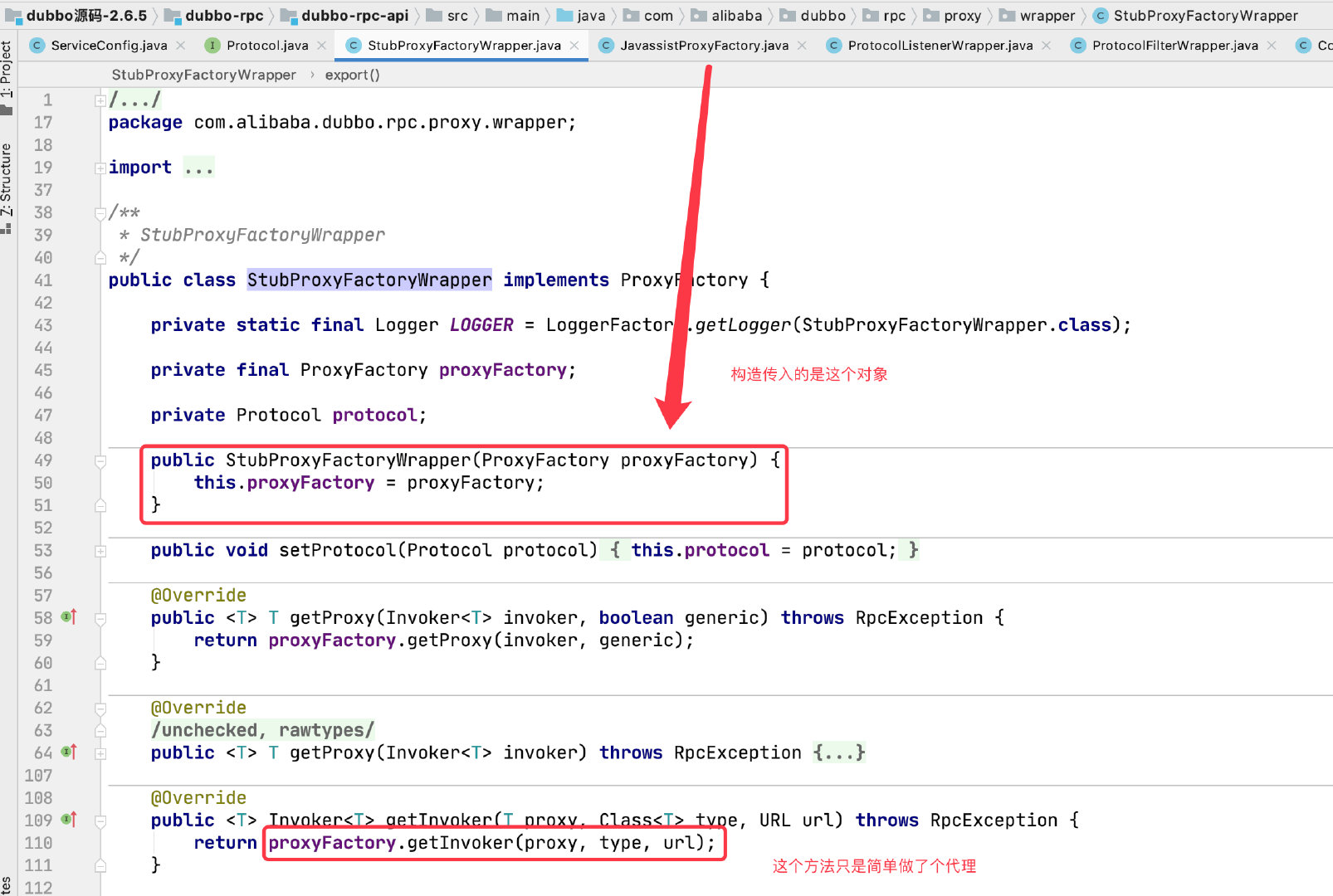
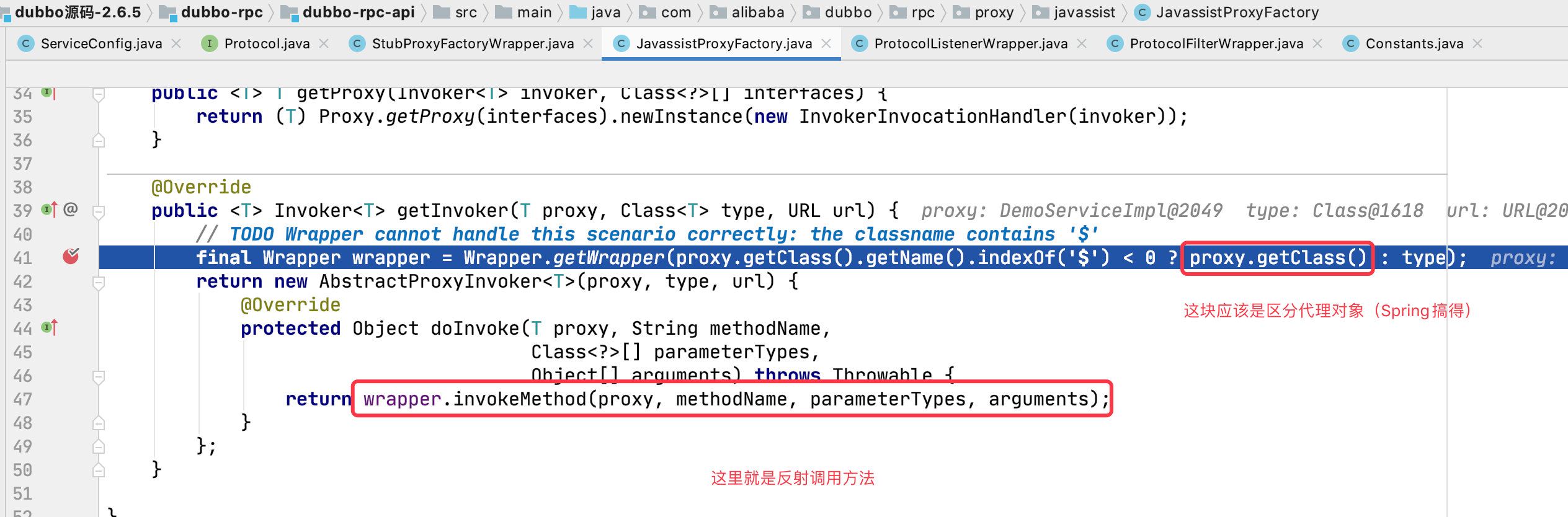
注:此处 Wrapper 对象的实现是 dubbo 使用 Javassist 生成的
作用:生成 Invoke 对象,Invoke 对象的作用就是在执行调用方法的时候可以执行过滤器链。
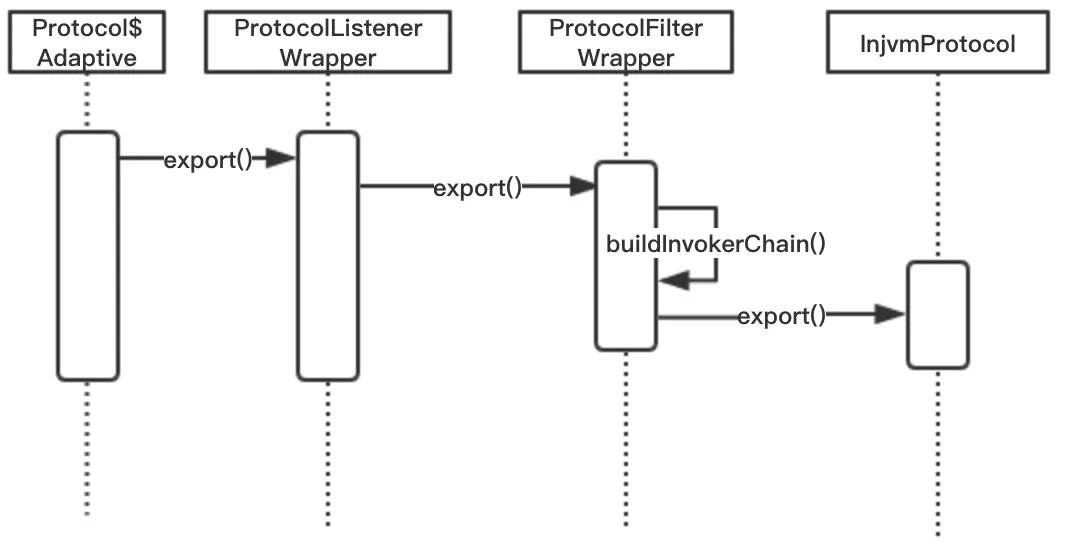
tag2 protocol.export(Invoker)
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Exporter export(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker arg0) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");
// 从Invoker 对象中获取到 url 对象
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
// 通过 url 对象获取协议
String extName = ( url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() );
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = null;
try {
// 获取到对应协议的对象 ProtocolFilterWrapper
extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
}catch(Exception e){
if (count.incrementAndGet() == 1) {
logger.warn("Failed to find extension named " + extName + " for type org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol, will use default extension dubbo instead.", e);
}
extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension("dubbo");
}
// 执行协议对象的 export() 方法
return extension.export(arg0);
}
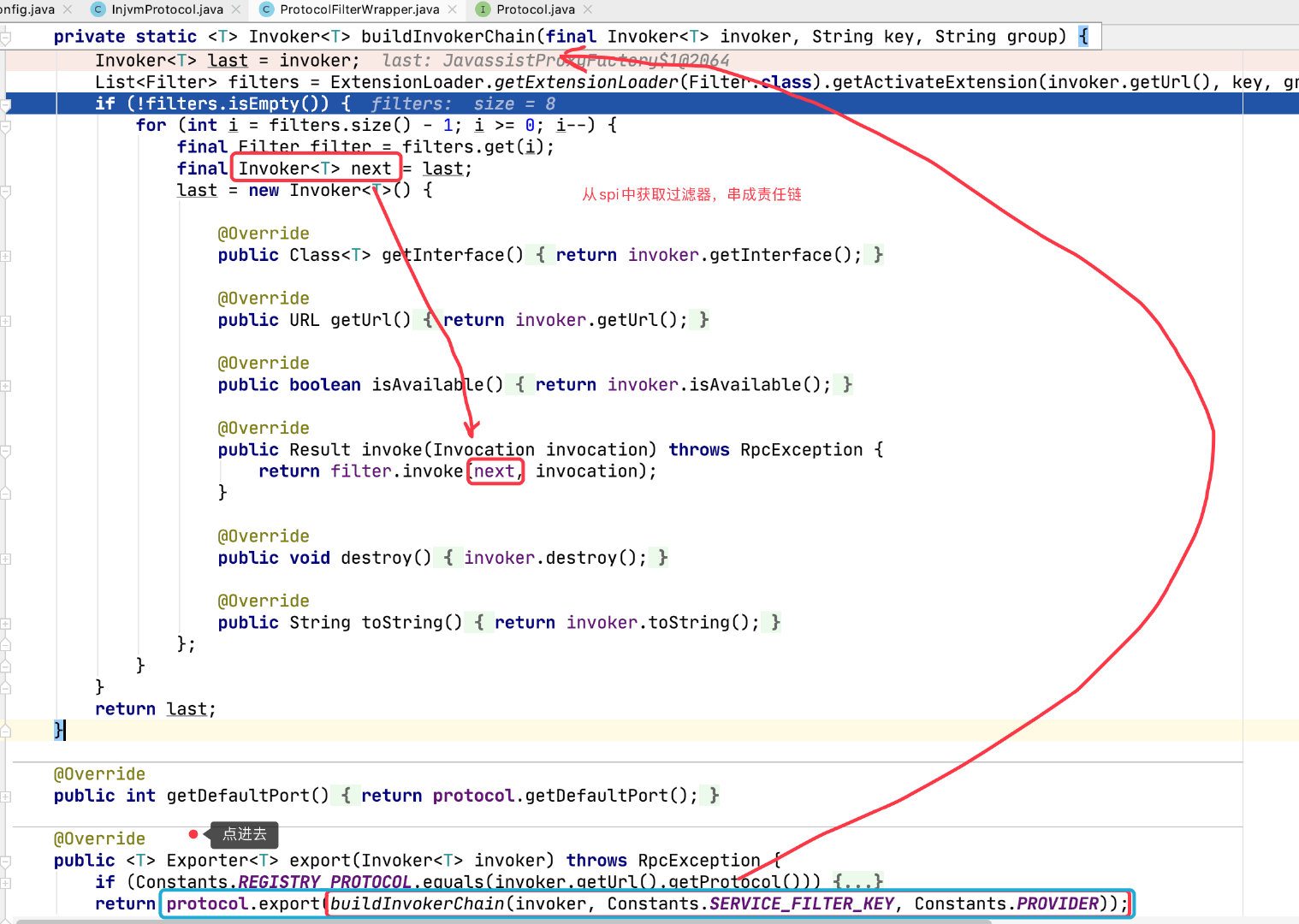
将 Filter 封装成了 Invoker,适配器模式
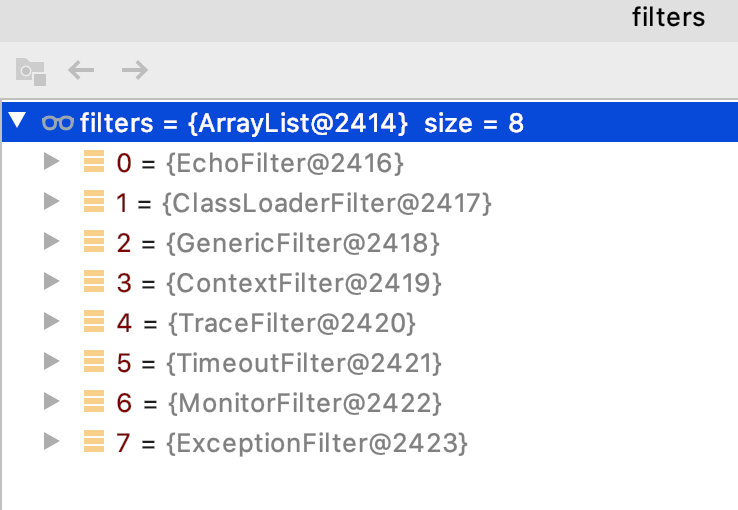
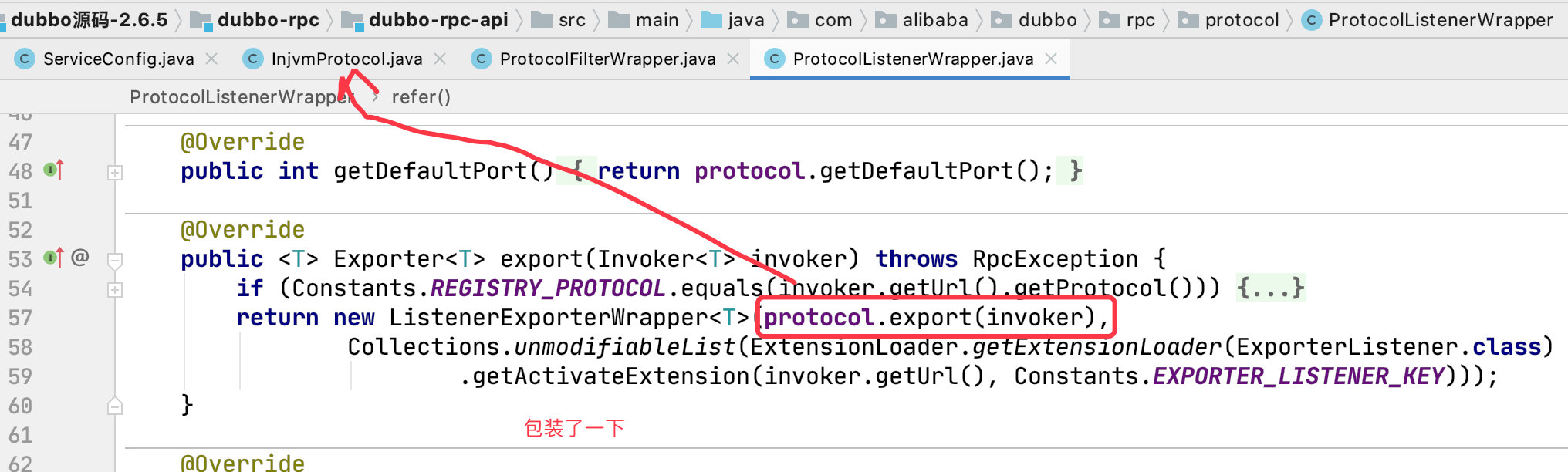

之后就将其加到了 exporters 集合中。
作用:为 Invoke 添加过滤器
本部分参考
三、服务引用(本地调用)
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- provider's application name, used for tracing dependency relationship -->
<dubbo:application name="demo-provider"/>
<!-- 本地调用:本地调用使用了 injvm 协议,是一个伪协议,它不开启端口,不发起远程调用,只在 JVM 内直接关联,但执行 Dubbo 的 Filter 链。
http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/user/demos/local-call.html
-->
<dubbo:provider protocol="injvm" registry="N/A"/>
<dubbo:reference id="demoService-consumer" check="false" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService"/>
<!-- use multicast registry center to export service -->
<!-- <dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>-->
<!-- use dubbo protocol to export service on port 20880 -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880"/>
<!-- service implementation, as same as regular local bean -->
<bean id="demoService" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoServiceImpl"/>
<!-- declare the service interface to be exported -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" ref="demoService"/>
</beans>
我们先去官网看下 <dubbo:reference> 的注释:
标签对应服务消费者引用服务配置。对应的配置类: org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig
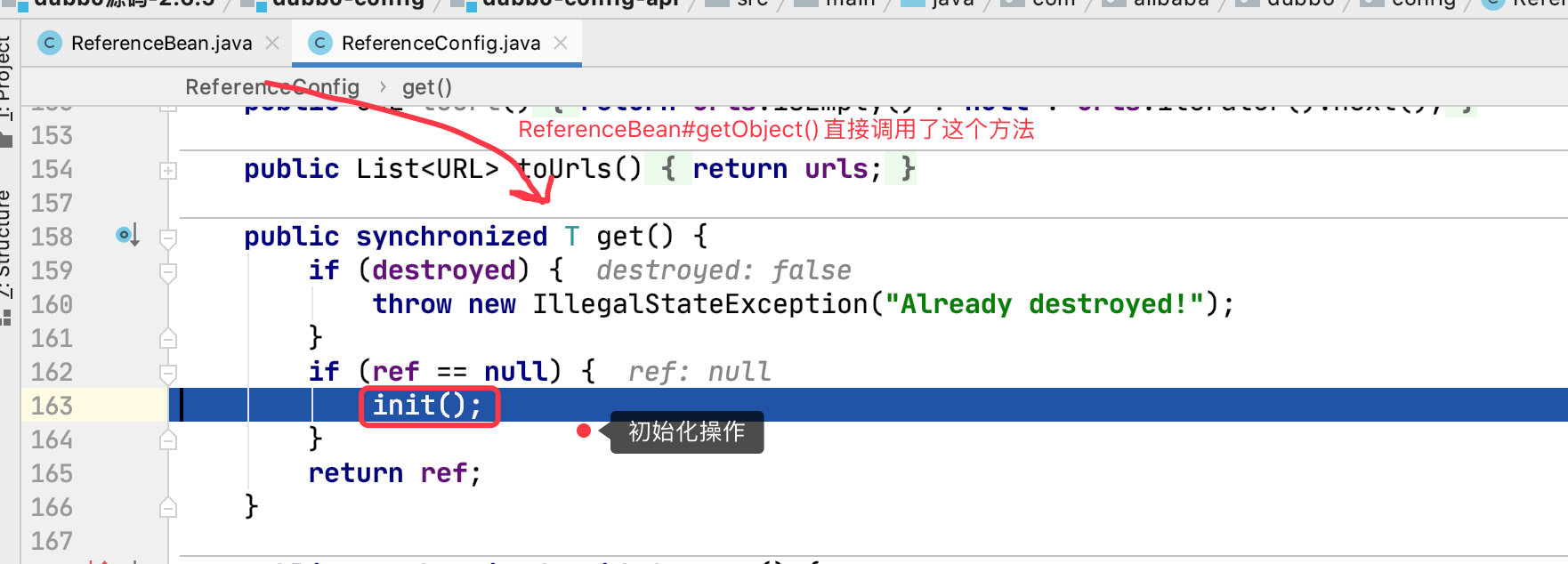
public class ReferenceBean<T> extends ReferenceConfig<T>
implements FactoryBean, // 如果是 FactoryBean 类型,获取对象时会调用它的 getObject 方法
ApplicationContextAware, // 注入 ApplicationContext
InitializingBean, // 对象初始化之后调用
DisposableBean // 对象销毁前调用
DubboBeanDefinitionParser#parse() 部分代码我们就不分析了,上面已经说了,我们先来看 FactoryBean#getObject();
private void init() {
// 避免重复初始化
if (initialized) {
return;
}
initialized = true;
// 检测接口名合法性
if (interfaceName == null || interfaceName.length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("interface not allow null!");
}
/*
检测 ConsumerConfig 实例是否存在,如不存在则创建一个新的实例,然后通过系统变量或 dubbo.properties 配置文件填充 ConsumerConfig 的字段。
接着是检测泛化配置,并根据配置设置 interfaceClass 的值。
*/
// <dubbo:consumer> 服务消费者缺省值配置。配置类: org.apache.dubbo.config.ConsumerConfig 。同时该标签为 <dubbo:reference> 标签的缺省值设置。
// http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/user/references/xml/dubbo-consumer.html
// 检测 consumer 变量是否为空,为空则创建
checkDefault();
appendProperties(this);
if (getGeneric() == null && getConsumer() != null) {
// 设置 generic
setGeneric(getConsumer().getGeneric());
}
// 检测是否为泛化接口
if (ProtocolUtils.isGeneric(getGeneric())) {
interfaceClass = GenericService.class;
} else {
try {
// 加载类
interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, true, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
// 检查 <dubbo:method> 中配置的那些方法存不存在
checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods);
}
// -------------------------------✨ 分割线1 ✨------------------------------
/*
这段逻辑用于从系统属性或配置文件中加载与接口名相对应的配置,并将解析结果赋值给 url 字段。url 字段的作用一般是用于点对点调用
*/
// 从系统变量中获取与接口名对应的属性值
String resolve = System.getProperty(interfaceName);
String resolveFile = null;
if (resolve == null || resolve.length() == 0) {
// 从系统属性中获取解析文件路径
resolveFile = System.getProperty("dubbo.resolve.file");
if (resolveFile == null || resolveFile.length() == 0) {
// 从指定位置加载配置文件
File userResolveFile = new File(new File(System.getProperty("user.home")), "dubbo-resolve.properties");
if (userResolveFile.exists()) {
// 获取文件绝对路径
resolveFile = userResolveFile.getAbsolutePath();
}
}
if (resolveFile != null && resolveFile.length() > 0) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(new File(resolveFile));
// 从文件中加载配置
properties.load(fis);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unload ..., cause:...");
} finally {
try {
if (null != fis) fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
// 获取与接口名对应的配置
resolve = properties.getProperty(interfaceName);
}
}
if (resolve != null && resolve.length() > 0) {
// 将 resolve 赋值给 url
url = resolve;
}
// -------------------------------✨ 分割线2 ✨------------------------------
/* 检测几个核心配置类是否为空,为空则尝试从其他配置类中获取 */
if (consumer != null) {
if (application == null) {
// 从 consumer 中获取 Application 实例,下同
application = consumer.getApplication();
}
if (module == null) {
module = consumer.getModule();
}
if (registries == null) {
registries = consumer.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = consumer.getMonitor();
}
}
if (module != null) {
if (registries == null) {
registries = module.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = module.getMonitor();
}
}
if (application != null) {
if (registries == null) {
registries = application.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = application.getMonitor();
}
}
// 检测 Application 合法性
checkApplication();
// 检测本地存根配置合法性
checkStubAndMock(interfaceClass);
// -------------------------------✨ 分割线3 ✨------------------------------
/* 收集各种配置,并将配置存储到 map 中 */
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
Map<Object, Object> attributes = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
// 添加 side、协议版本信息、时间戳和进程号等信息到 map 中
map.put(Constants.SIDE_KEY, Constants.CONSUMER_SIDE);
map.put(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY, Version.getProtocolVersion());
map.put(Constants.TIMESTAMP_KEY, String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()));
if (ConfigUtils.getPid() > 0) {
map.put(Constants.PID_KEY, String.valueOf(ConfigUtils.getPid()));
}
// 非泛化服务
if (!isGeneric()) {
// 获取版本
String revision = Version.getVersion(interfaceClass, version);
if (revision != null && revision.length() > 0) {
map.put("revision", revision);
}
// 获取接口方法列表,并添加到 map 中
String[] methods = Wrapper.getWrapper(interfaceClass).getMethodNames();
if (methods.length == 0) {
map.put("methods", Constants.ANY_VALUE);
} else {
map.put("methods", StringUtils.join(new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(methods)), ","));
}
}
map.put(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, interfaceName);
// 将 ApplicationConfig、ConsumerConfig、ReferenceConfig 等对象的字段信息添加到 map 中
appendParameters(map, application);
appendParameters(map, module);
appendParameters(map, consumer, Constants.DEFAULT_KEY);
appendParameters(map, this);
// -------------------------------✨ 分割线4 ✨------------------------------
/* 处理 MethodConfig 实例。该实例包含了事件通知配置,比如 onreturn、onthrow、oninvoke 等 */
String prefix = StringUtils.getServiceKey(map);
// 将 <dubbo:method> 中配置的哪些东西放进 attributes 中,然后加进 map 中
if (methods != null && !methods.isEmpty()) {
// 遍历 MethodConfig 列表
for (MethodConfig method : methods) {
appendParameters(map, method, method.getName());
String retryKey = method.getName() + ".retry";
// 检测 map 是否包含 methodName.retry
if (map.containsKey(retryKey)) {
String retryValue = map.remove(retryKey);
if ("false".equals(retryValue)) {
// 添加重试次数配置 methodName.retries
map.put(method.getName() + ".retries", "0");
}
}
// 添加 MethodConfig 中的“属性”字段到 attributes
// 比如 onreturn、onthrow、oninvoke 等
appendAttributes(attributes, method, prefix + "." + method.getName());
checkAndConvertImplicitConfig(method, map, attributes);
}
}
// -------------------------------✨ 分割线5 ✨------------------------------
/* 主要用于解析服务消费者 ip,以及调用 createProxy 创建代理对象 */
// 获取服务消费者 ip 地址
String hostToRegistry = ConfigUtils.getSystemProperty(Constants.DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY);
if (hostToRegistry == null || hostToRegistry.length() == 0) {
hostToRegistry = NetUtils.getLocalHost();
} else if (isInvalidLocalHost(hostToRegistry)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Specified invalid registry ip from property..." );
}
map.put(Constants.REGISTER_IP_KEY, hostToRegistry);
// 存储 attributes(和<dubbo:method>有关,不知道要干啥) 到系统上下文中
StaticContext.getSystemContext().putAll(attributes);
// 创建代理类
// injvm://127.0.0.1/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?application=demo-provider&check=false&dubbo=2.0.2
// &interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=32089&qos.port=22222
// ®ister.ip=192.168.2.94&side=consumer×tamp=1589444555032
ref = createProxy(map);
// 根据服务名,ReferenceConfig,代理类构建 ConsumerModel,
// 并将 ConsumerModel 存入到 ApplicationModel 中
ConsumerModel consumerModel = new ConsumerModel(getUniqueServiceName(), this, ref, interfaceClass.getMethods());
ApplicationModel.initConsumerModel(getUniqueServiceName(), consumerModel);
}
这段代码不重要,主要看 createProxy(map) 方法:
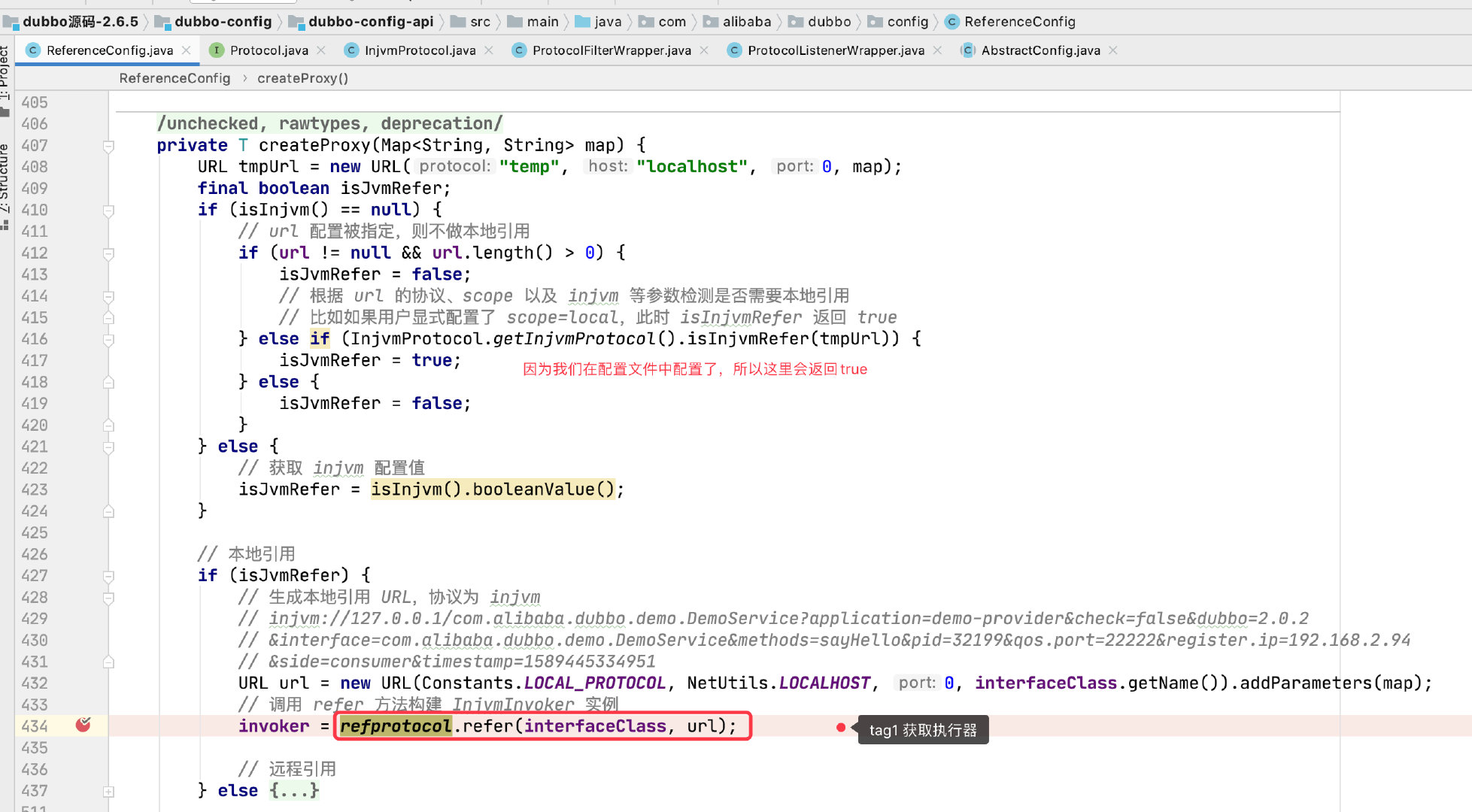
tag1 refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url);
调用的流程和上面一样,export() 方法改成了 refer 方法。
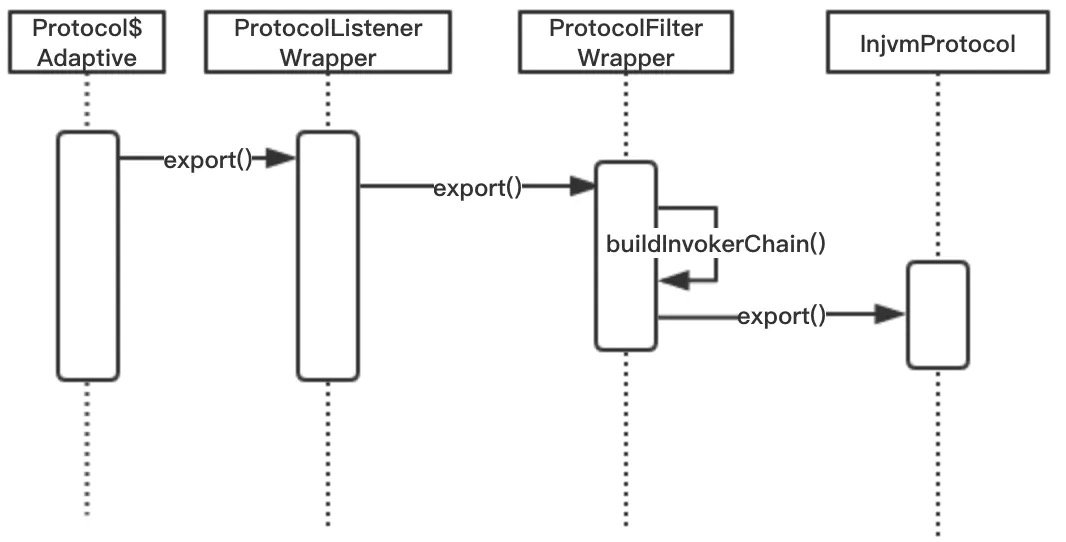
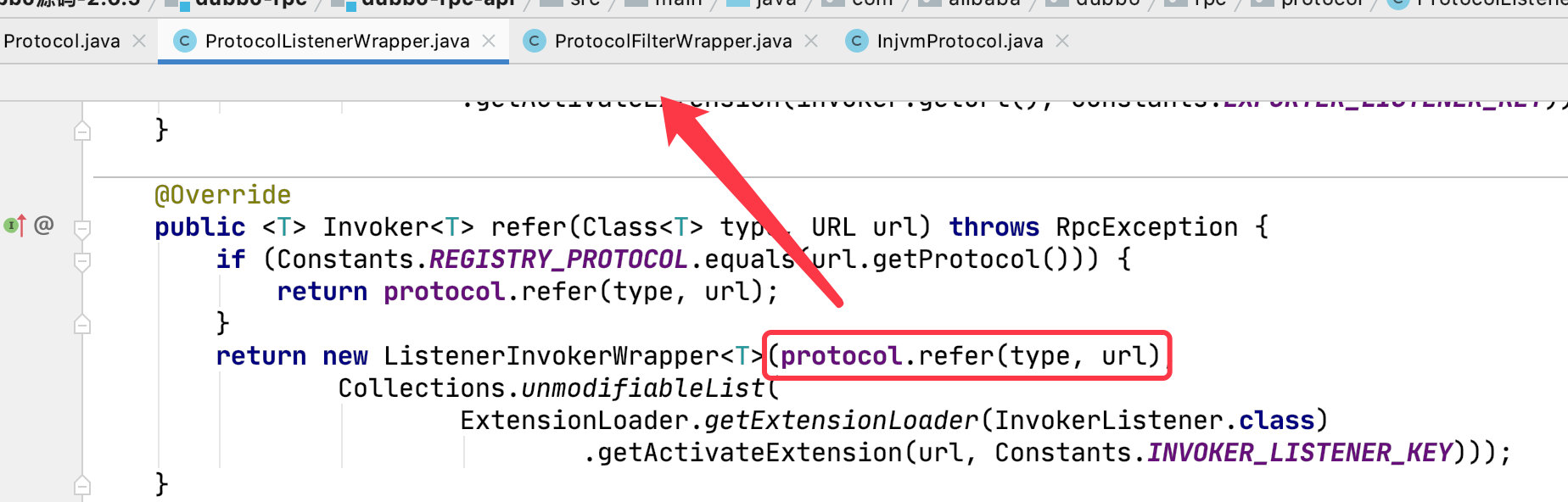
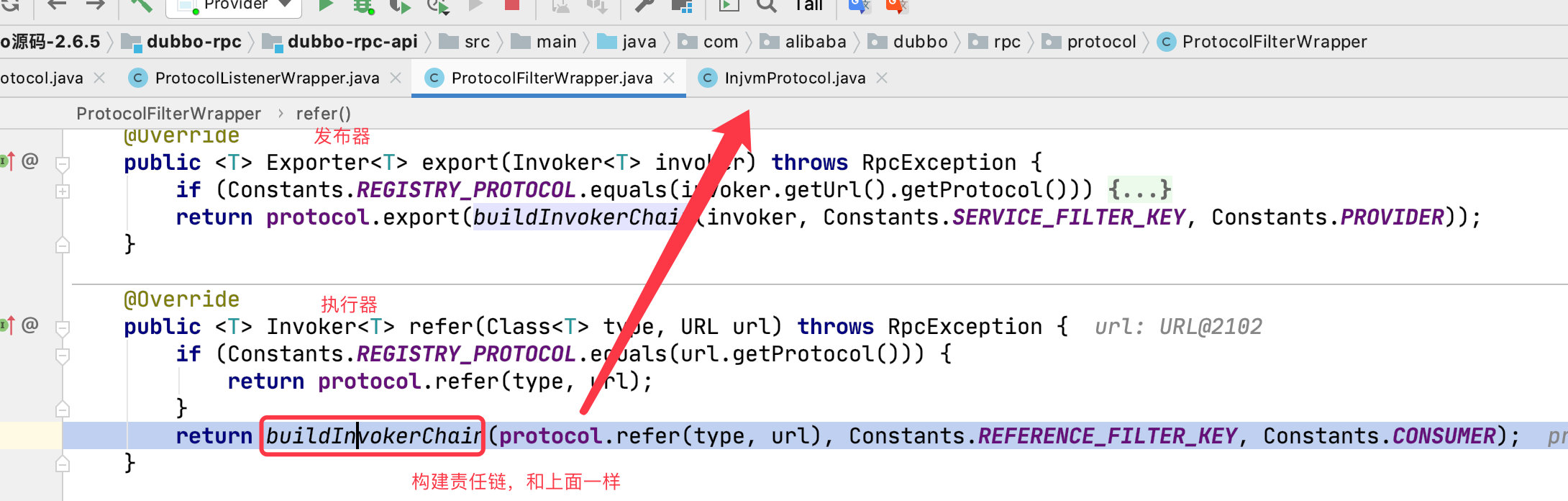
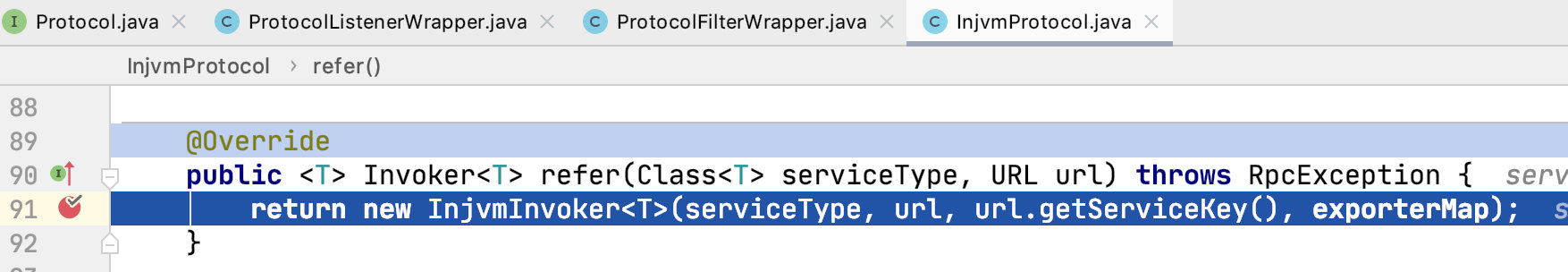
生成 Invoke
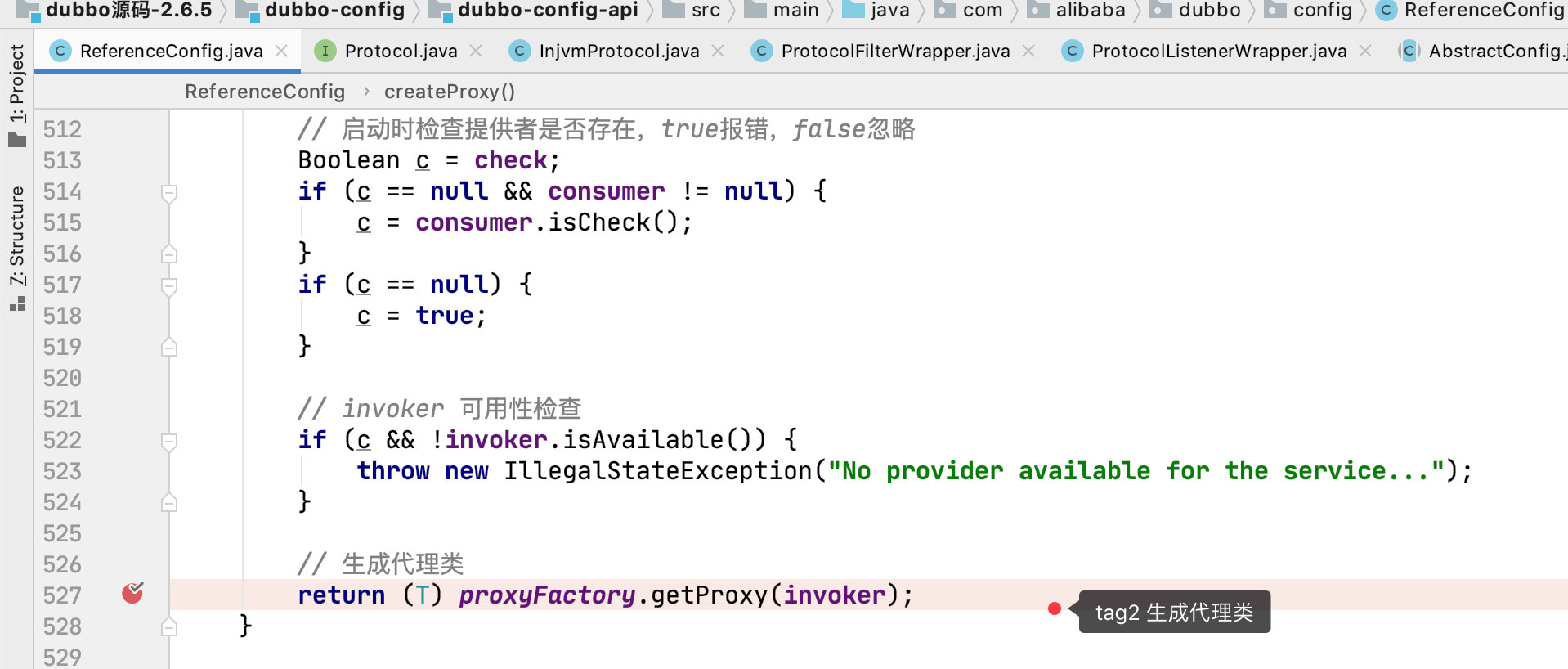
tag2 proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
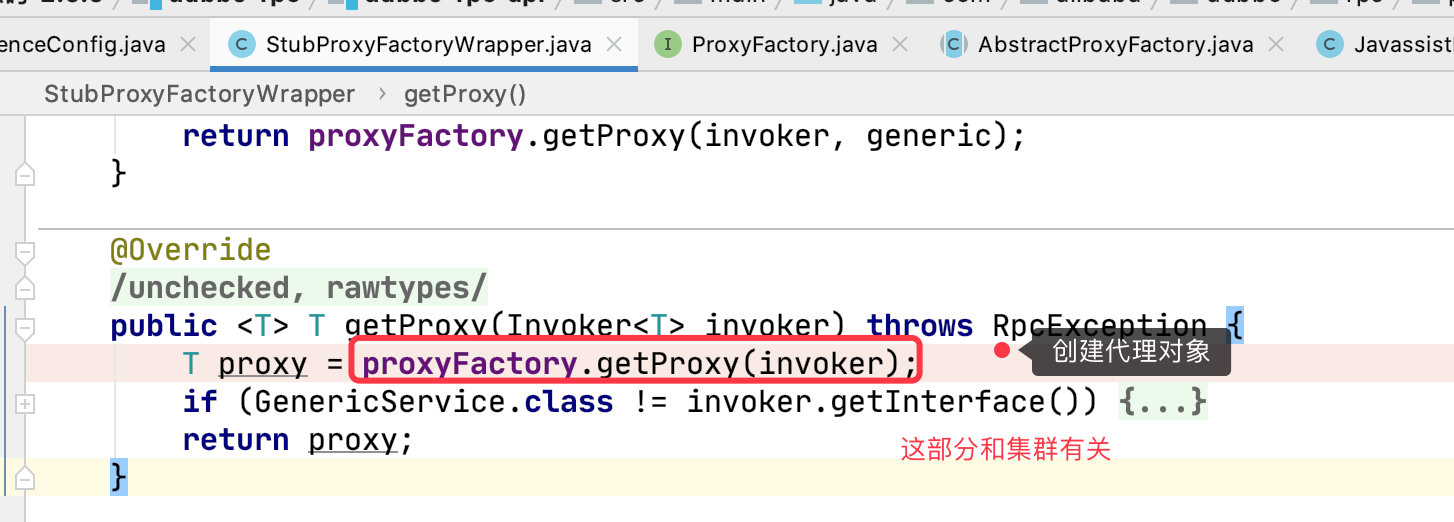
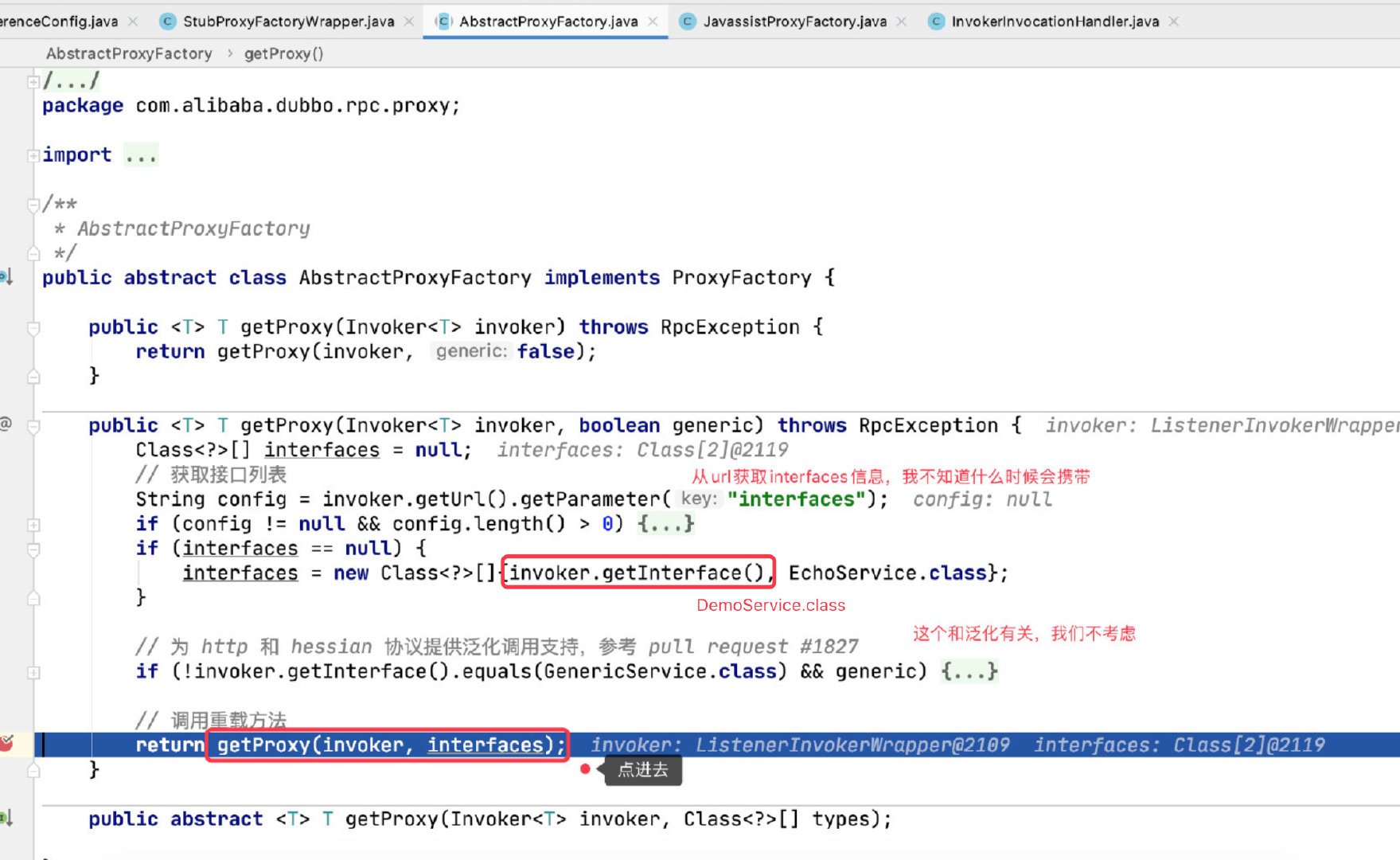
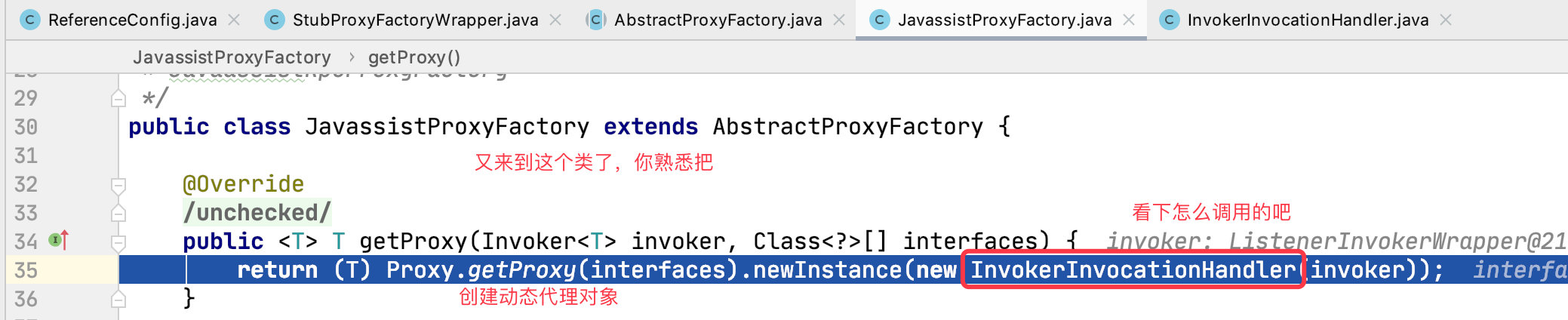
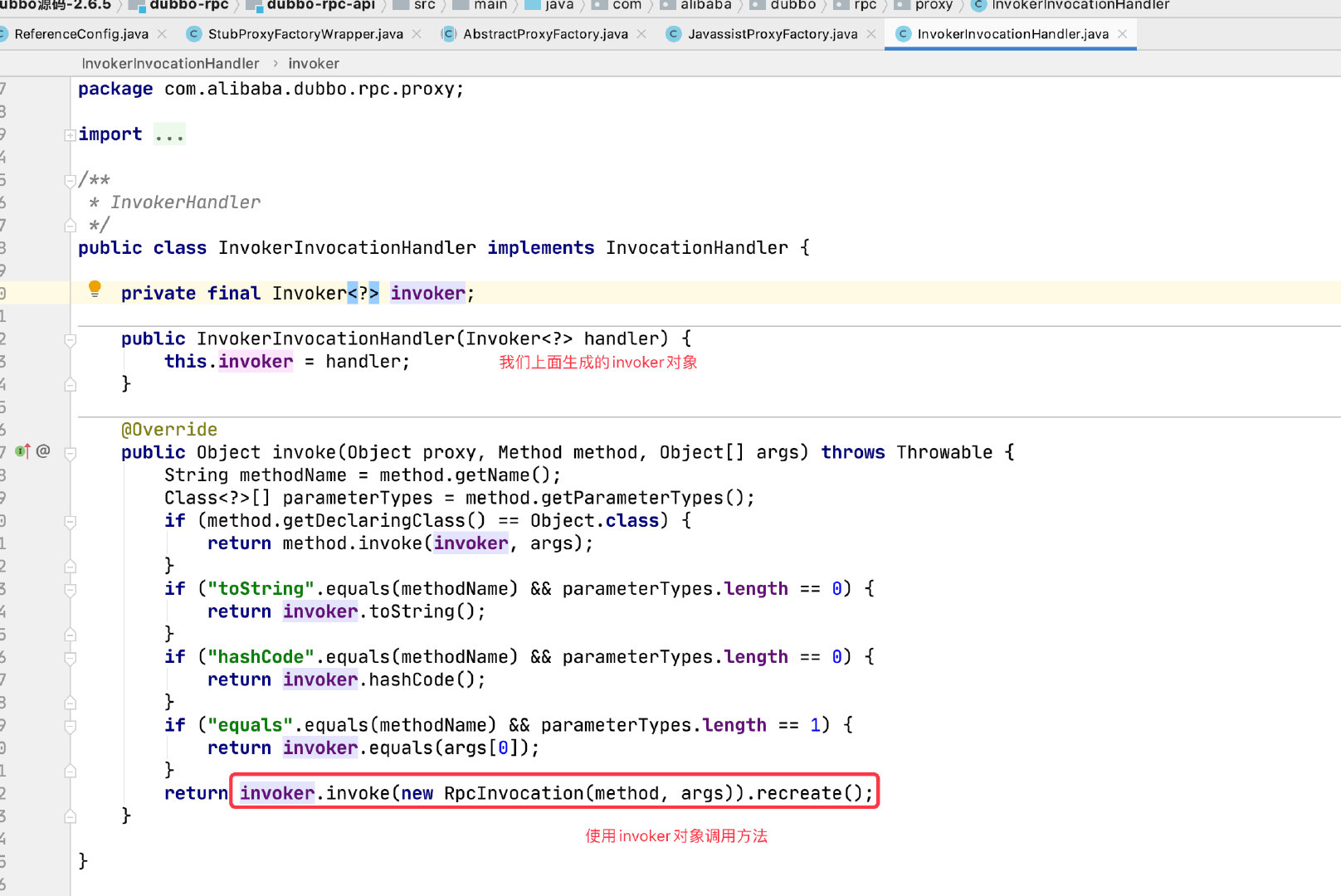
我们看下 Invoker 中是怎么写的吧
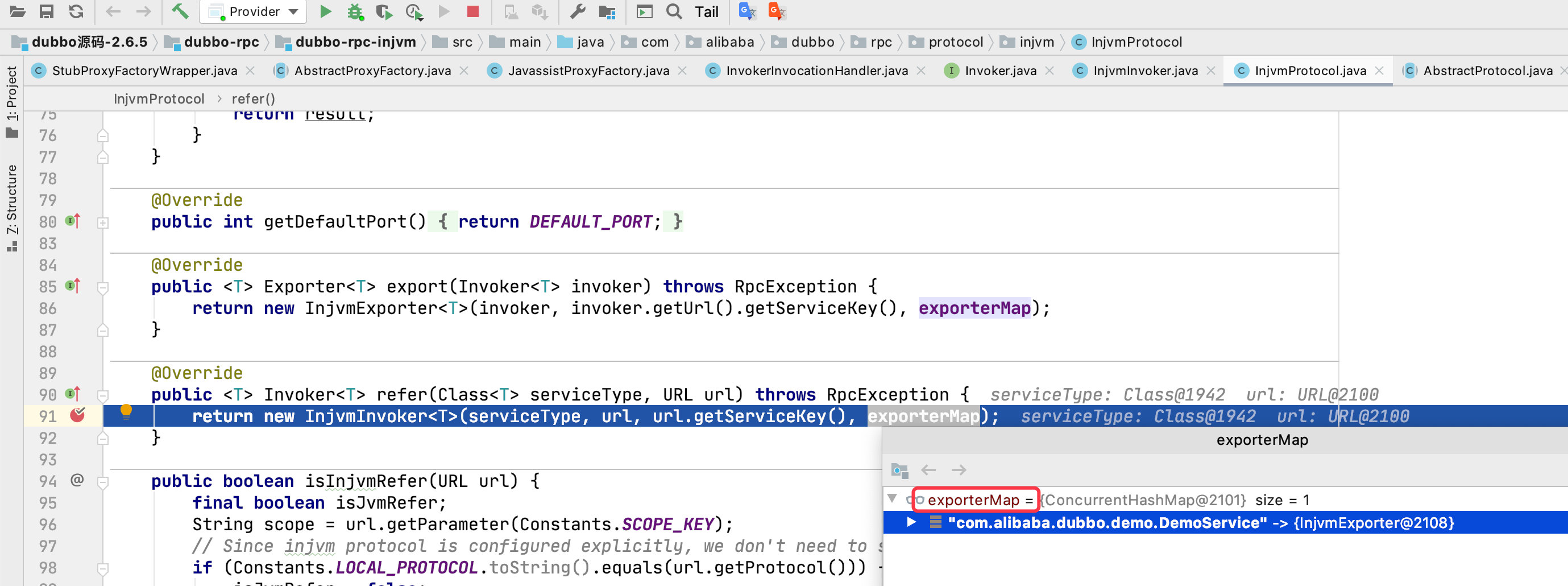
exporterMap 的 value 是发布器对象(Exporter),就是我们上面发布的那个。

我们接一下上面那张图:

通过这个对象,完成方法的调用。
本部分参考
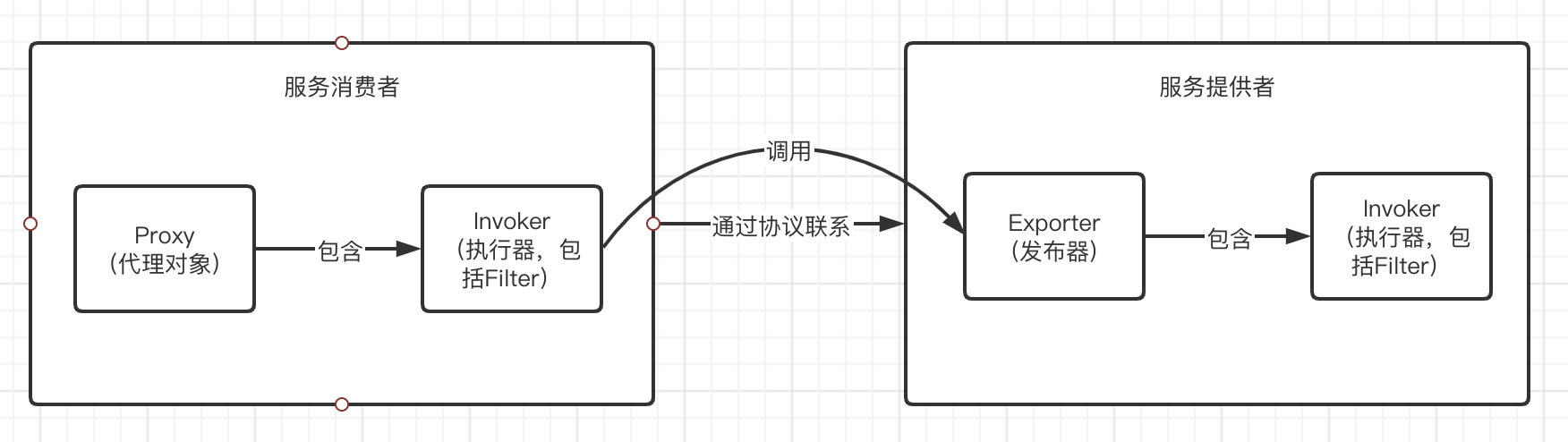
Invoker:封装要执行的方法和过滤器
Exporter:用来对外发布一个 Invoker
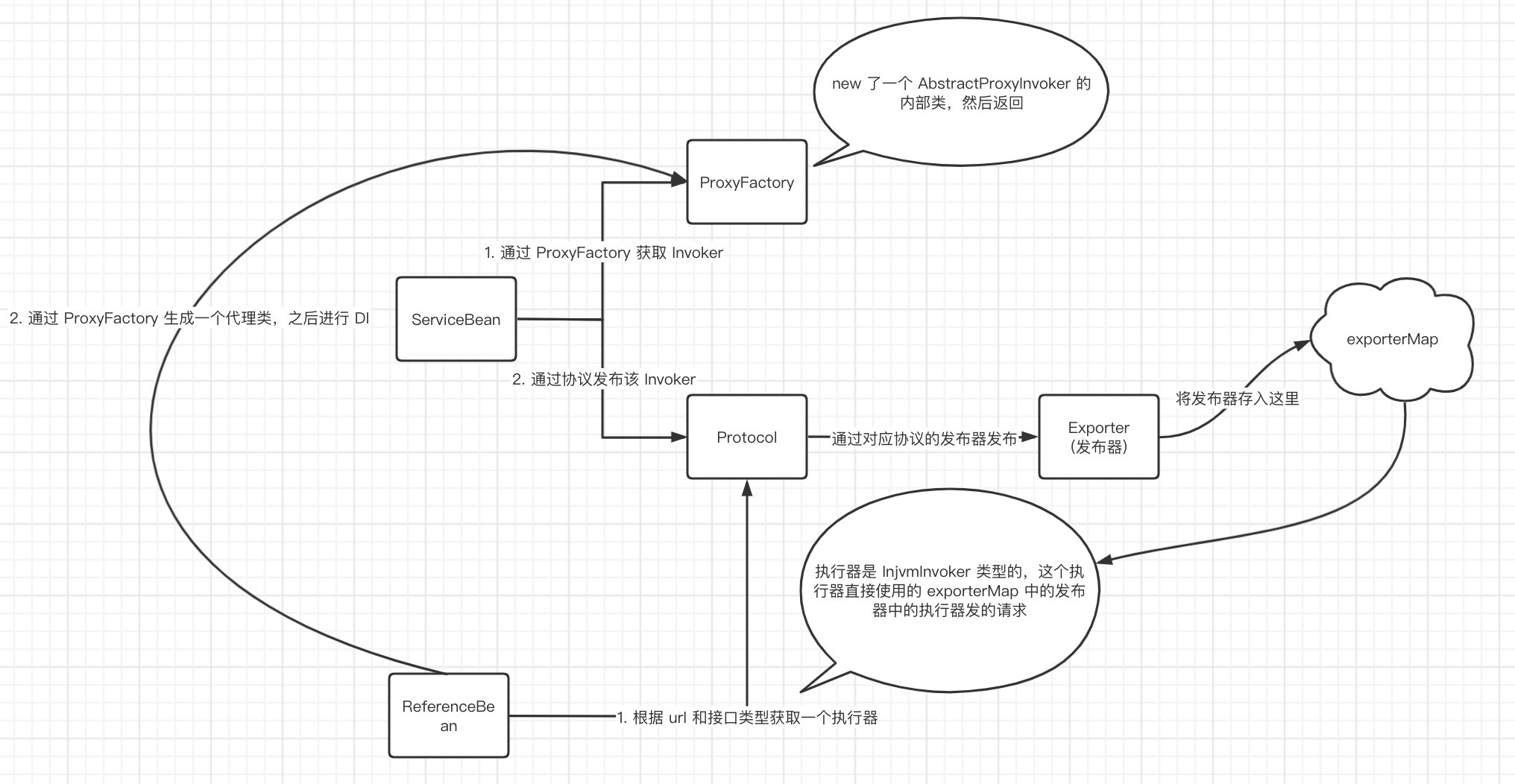
ServiceBean 在初始化(Init#afterProperties())的时候,从代理工厂中获取了一个 Invoker,这个 Invoker 的作用就是在服务提供者那端通过反射调用服务消费者调用的方法,之后找出用户配置的协议,通过协议中的发布器对外发布(injvm 就是存到一个 map 中,dubbo 协议就是暴露一个服务)
ReferenceBean 在初始化(FactoryBean#getObject())的时候,根据用户配置的协议,获取到了一个协议对象,通过这个协议获取一个 Invoker 对象(其中包裹着 dubbo:服务调用,injvm:从 map 中取出发布器中的 Invoker 进行执行)。
这里的 Invoker 对象已经就是我们最终调用方法时使用的对象,但是我们要进行依赖注入啊,Invoker 对象并不是我们依赖注入的类型,所以又要通过代理工厂创建一个代理对象,之后才进行 DI
本集完
2020/11/13读后感:
ServiceBean 被 Spring 创建完成的时候做了以下几件事:
- 创建 invoker 对象,其中的方法是根据方法名和参数反射
- 创建 export 对象,并将其对外发布
当我们对标注着 @Refrence 注解进行依赖注入的时候做了以下几件事:
- 创建 invoker 对象,将调用的一些信息(serviceKey)注入 invoker 对象中
- 创建代理对象,当用户调用的时候调用 invoker#invoke() 方法
服务调用时做了以下几件事:
- 代理对象调用 invoker#invoke() 方法
- 父类(AbstractInvoker)会调用子类(例如 InjvmInvoker)的 doInvoke 方法,不同的子类会通过不同的方式调用服务提供者对外暴露的 export 对象
- 服务提供者会调用 export 对象中的 invoker 对象的 invoke() 方法
 IDEA激活码
IDEA激活码


