7.3.7 线程安全集合类概述
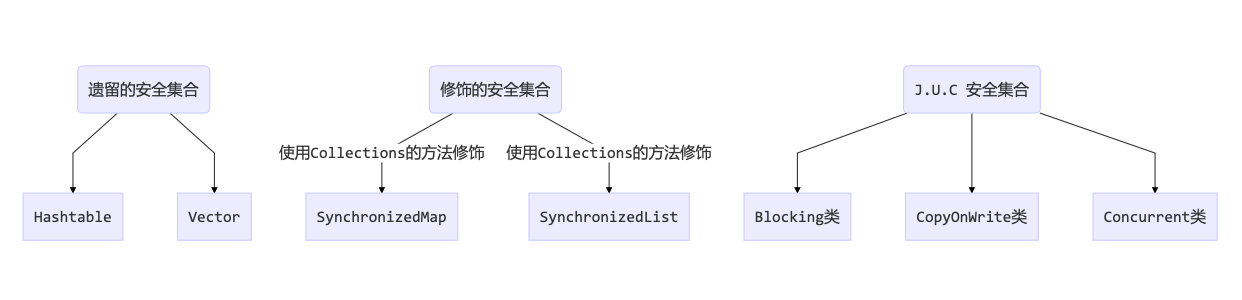
重点介绍 java.util.concurrent.* 下的线程安全集合类,可以发现它们有规律,里面包含三类关键词:Blocking、CopyOnWrite、Concurrent
- Blocking 大部分实现基于锁,并提供用来阻塞的方法
- CopyOnWrite 之类容器修改开销相对较重
- Concurrent 类型的容器
- 内部很多操作使用 cas 优化,一般可以提供较高吞吐量
- 弱一致性
- 遍历时弱一致性,例如,当利用迭代器遍历时,如果容器发生修改,迭代器仍可以继续进行遍历,这时内容是旧的
- 求大小弱一致性,size 操作未必是 100% 准确
- 读取弱一致性
注:遍历时如果发生了修改,对于非安全容器来讲,使用 fail-fast 机制也就是让遍历立刻失败,抛出 ConcurrentModificationException,不再继续遍历
7.3.8 ConcurrentHashMap
重要属性和内部类
// 默认为 0
// 当初始化时, 为 -1
// 当扩容时, 为 -(1 + 扩容线程数)
// 当初始化或扩容完成后,为 下一次的扩容的阈值大小
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
// 整个 ConcurrentHashMap 就是一个 Node[]
static class Node<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V> {
}
// hash 表
transient volatile Node<K, V>[] table;
// 扩容时的 新 hash 表
private transient volatile Node<K, V>[] nextTable;
// 扩容时如果某个 bin 迁移完毕, 用 ForwardingNode 作为旧 table bin 的头结点
// 作用 1. 标识当前桶已经移完,2. 当迁移的时候有人get(key)看到这个标记,就知道去新数组中找了
static final class ForwardingNode<K, V> extends Node<K, V> {
}
// 用在 compute 以及 computeIfAbsent 时, 用来占位, 计算完成后替换为普通 Node
static final class ReservationNode<K, V> extends Node<K, V> {
}
// 作为 treebin 的头节点, 存储 root 和 first
static final class TreeBin<K, V> extends Node<K, V> {
}
// 作为 treebin 的节点, 存储 parent, left, right
static final class TreeNode<K, V> extends Node<K, V> {
}
重要方法
// 获取 Node[] 中第 i 个 Node
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i)
// cas 修改 Node[] 中第 i 个 Node 的值, c 为旧值, v 为新值
static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v)
// 直接修改 Node[] 中第 i 个 Node 的值, v 为新值
static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v)
构造器分析
可以看到实现了懒惰初始化,在构造方法中仅仅计算了 table 的大小,以后在第一次使用时才会真正创建
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 当初始容量小于并发度时,将初始容量设为并发度的大小
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
// 计算Map的容量
long size = (long) (1.0 + (long) initialCapacity / loadFactor);
// tableSizeFor 仍然是保证计算的大小是 2^n, 即 16,32,64 ...
int cap = (size >= (long) MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int) size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
get 流程
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K, V>[] tab;
Node<K, V> e, p;
int n, eh;
K ek;
// spread 方法能确保返回结果是正数,因为负数在后续有额外的用途
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
// 按位与运算,相当于取模
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
// 如果头结点已经是要查找的 key
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))) return e.val;
}
// hash 为负数表示该 bin 在扩容中(-1)或是 treebin(-2), 这时调用 find 方法来查找
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
// 正常遍历链表, 用 equals 比较
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
put 流程
以下数组简称(table),链表简称(bin)
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 其中 spread 方法会综合高位低位, 具有更好的 hash 性
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K, V>[] tab = table; ; ) {
// f 是链表头节点
// fh 是链表头结点的 hash
// i 是链表在 table 中的下标
Node<K, V> f;
int n, i, fh;
// 要创建 table
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
// 初始化 table 使用了 cas, 无需 synchronized 创建成功, 进入下一轮循环
tab = initTable();
// 要创建链表头节点
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
// 添加链表头使用了 cas, 无需 synchronized
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, null))) break;
}
// 帮忙扩容
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
// 帮忙之后, 进入下一轮循环
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null; // 锁住链表头节点
synchronized (f) {
// 再次确认链表头节点没有被移动
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
// 链表
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
// 遍历链表
for (Node<K, V> e = f; ; ++binCount) {
K ek;
// 找到相同的 key
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
// 更新
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K, V> pred = e;
// 已经是最后的节点了, 新增 Node, 追加至链表尾
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 红黑树
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K, V> p;
binCount = 2;
// putTreeVal 会看 key 是否已经在树中, 是, 则返回对应的 TreeNode
if ( (p = ((TreeBin<K, V>) f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value))!=null){
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value;
}
}
// 释放链表头节点的锁
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
// 如果链表长度 >= 树化阈值(8), 进行链表转为红黑树
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
// 增加 size 计数
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
private final Node<K, V>[] initTable() {
Node<K, V>[] tab;
int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) Thread.yield();
// 尝试将 sizeCtl 设置为 -1(表示初始化 table)
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
// 获得锁, 创建 table, 这时其它线程会在 while() 循环中 yield 直至 table 创建
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
Node<K, V>[] nt = (Node<K, V>[]) new Node<?, ?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
ConcurrentHashMap.CounterCell[] as;
long b, s;
if ( // 已经有了 counterCells, 向cell累加
(as = counterCells) != null ||
// 还没有, 向 baseCount 累加
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
ConcurrentHashMap.CounterCell a;
long v;
int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if ( // 还没有 counterCells;上面的if不是已经判断!=null了吗?
as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
// 还没有cell
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
// cell cas 增加计数失败
!(uncontended = U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
// 创建累加单元数组和cell, 累加重试
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
// 获取元素个数
s = sumCount();
}
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K, V>[] tab, nt;
int n, sc;
while (s >= (long) (sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 || sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null || transferIndex <= 0)
break;
// newtable 已经创建了,帮忙扩容
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
// 需要扩容,这时 newtable 未创建
} else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2)) {
transfer(tab, null);
}
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
size 计算流程
size 计算实际发生在 put,remove 改变集合元素的操作之中,他和LongAdder很像
- 没有竞争发生,向 baseCount 累加计数
- 有竞争发生,新建 counterCells,向其中的一个 cell 累加计数
- counterCells 初始有两个
- cell 如果计数竞争比较激烈,会创建新的 cell 来累加计数
public int size() {
long n = sumCount();
return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :
(n > (long) Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : (int) n);
}
final long sumCount() {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells;
CounterCell a;
// 将 baseCount 计数与所有 cell 计数累加
long sum = baseCount;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
}
}
return sum;
}
Java 8 数组(Node) +(链表 Node | 红黑树 TreeNode)以下数组简称(table),链表简称(bin)
- 初始化,使用 cas 来保证并发安全,懒惰初始化 table
-树化,当 table.length < 64 时,先尝试扩容,超过 64 时,并且 bin.length > 8 时,会将链表树化,树化过程 会用 synchronized 锁住链表头 - put,如果该 bin 尚未创建,只需要使用 cas 创建 bin;如果已经有了,锁住链表头进行后续 put 操作,元素 添加至 bin 的尾部
- get,无锁操作仅需要保证可见性,扩容过程中 get 操作拿到的是 ForwardingNode 它会让 get 操作在新 table 进行搜索
- 扩容,扩容时以 bin 为单位进行,需要对 bin 进行 synchronized,但这时妙的是其它竞争线程也不是无事可做,它们会帮助把其它 bin 进行扩容,扩容时平均只有 1/6 的节点会把复制到新 table 中
- size,元素个数保存在 baseCount 中,并发时的个数变动保存在 CounterCell[] 当中。最后统计数量时累加即可
7.3.9 LinkedBlockingQueue
public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
static class Node<E> {
E item;
/**
* 下列三种情况之一
* - 真正的后继节点
* - 自己, 发生在出队时
* - null, 表示是没有后继节点, 是最后了
*/
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) {
item = x;
}
}
}
添加 & 移除元素流程
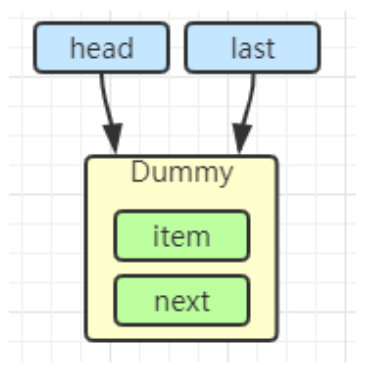
初始化链表 last = head = new Node<E>(null); Dummy 节点用来占位,item 为 null。(Dummy 节点作用是,始终保持了有一个节点可以继续往下挂接,不需要和消费者争抢锁)
当一个节点入队 last = last.next = node;(这句话是从右往左读的)
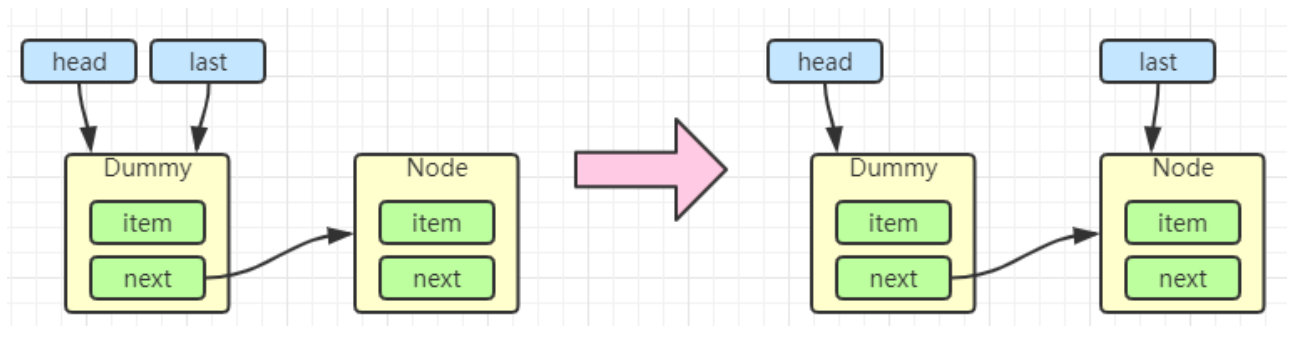
再来一个节点入队
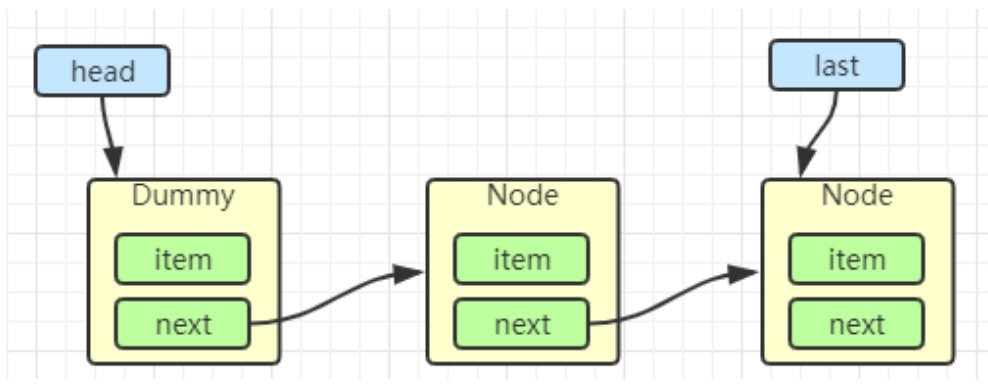
出队
Node<E> h = head;
Node<E> first = h.next;
h.next = h; // help GC
head = first;
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;
h = head
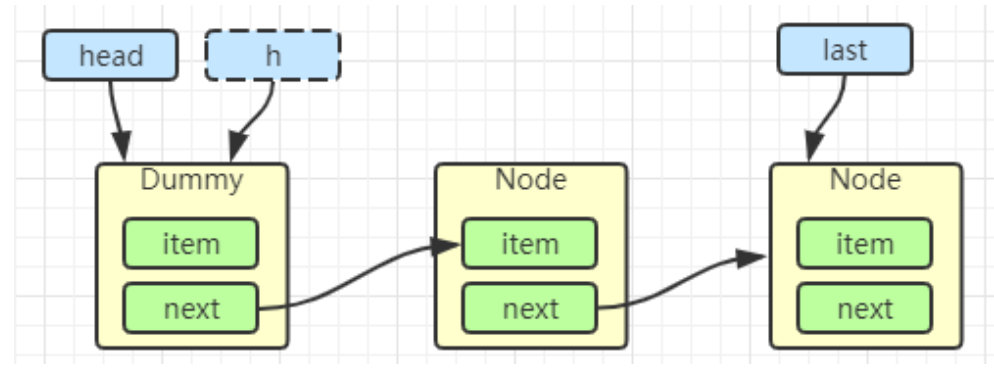
first = h.next
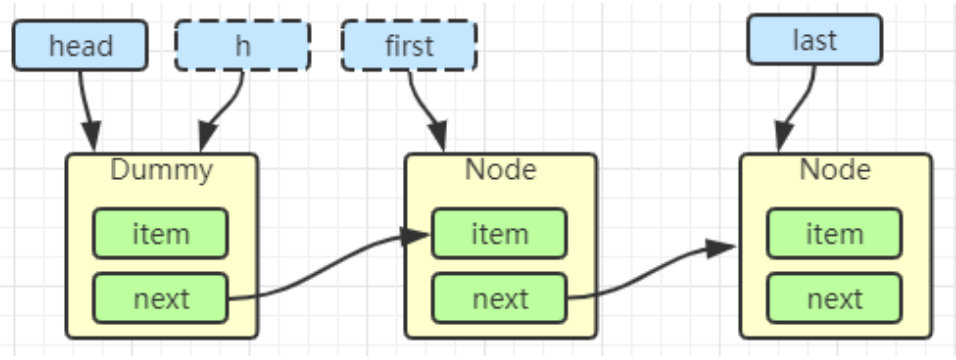
h.next = h
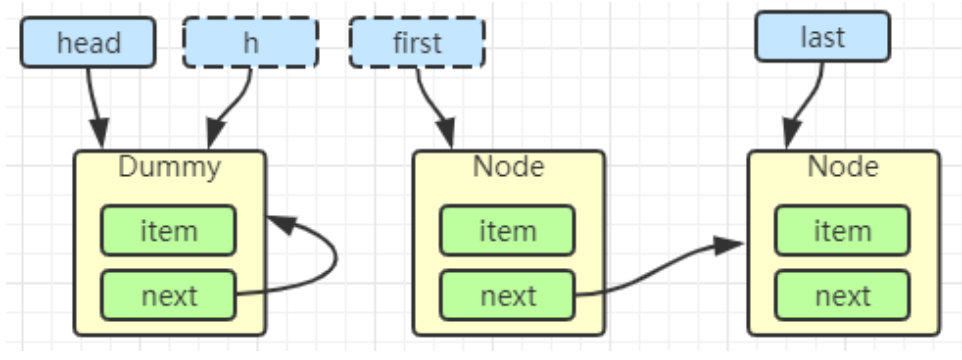
head = first
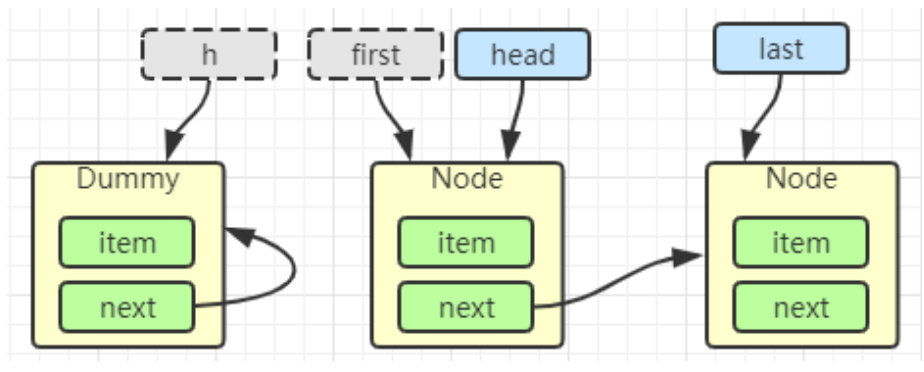
E x = first.item; first.item = null; return x;
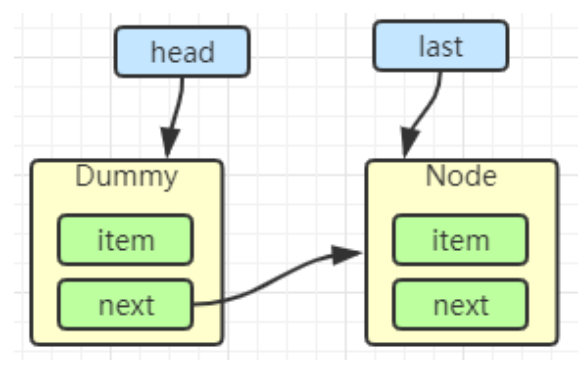
加锁分析
LinkedBQ设计的高明之处在于它用了两把锁和 dummy 节点
用一把锁,同一时刻,最多只允许有一个线程(生产者或消费者,二选一)执行
用两把锁,同一时刻,可以允许两个线程同时(一个生产者与一个消费者)执行
- 消费者与消费者线程仍然串行
- 生产者与生产者线程仍然串行
线程安全分析
- 当节点总数大于 2 时(包括 dummy 节点),putLock 保证的是 last 节点的线程安全,takeLock 保证的是 head 节点的线程安全。两把锁保证了入队和出队没有竞争
- 当节点总数等于 2 时(即一个 dummy 节点,一个正常节点)这时候,仍然是两把锁锁两个对象,不会竞争。(如果没有 dummy 节点,节点总数为1的时候,读写线程就需要用同一把锁锁住,否则会出现生产者挂载的节点,被消费者取走之后给删除了)
- 当节点总数等于 1 时(就一个 dummy 节点)这时 take 线程会被 notEmpty 条件阻塞,有竞争,会阻塞(采用 Condition)
源码
// 用于 put(阻塞) offer(非阻塞)
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
// 用户 take(阻塞) poll(非阻塞)
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
put 操作
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
// count 用来维护元素计数
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 满了等待
while (count.get() == capacity) {
// 倒过来读就好: 等待 notFull
notFull.await();
}
// 有空位, 入队且计数加一
enqueue(node);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// 除了自己 put 以外, 队列还有空位, 由自己叫醒其他 put 线程
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
// 如果队列中有一个元素, 叫醒 take 线程
if (c == 0)
// 这里调用的是 notEmpty.signal() 而不是 notEmpty.signalAll() 是为了减少竞争
signalNotEmpty();
}
take 操作:
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
E x;
int c = -1;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
// 如果队列中只有一个空位时, 叫醒 put 线程
// 如果有多个线程进行出队, 第一个线程满足 c == capacity, 但后续线程 c < capacity
if (c == capacity)
// 这里调用的是 notFull.signal() 而不是 notFull.signalAll() 是为了减少竞争
signalNotFull()
return x;
}
LinkedBlockingQueue VS ArrayBlockingQueue
- Linked 支持有界,Array 强制有界
- Linked 实现是链表,Array 实现是数组
- Linked 是懒惰的,而 Array 需要提前初始化 Node 数组
- Linked 每次入队会生成新 Node,而 Array 的 Node 是提前创建好的
- Linked 两把锁,Array 一把锁
7.3.10 ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 的设计与 LinkedBlockingQueue 非常像,也是
- 两把【锁】,同一时刻,可以允许两个线程同时(一个生产者与一个消费者)执行
- dummy 节点的引入让两把【锁】将来锁住的是不同对象,避免竞争
- 只是这【锁】使用了 cas 来实现
事实上,ConcurrentLinkedQueue 应用还是非常广泛的
例如之前讲的 Tomcat 的 Connector 结构时,Acceptor 作为生产者向 Poller 消费者传递事件信息时,正是采用了 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 将 SocketChannel 给 Poller 使用:
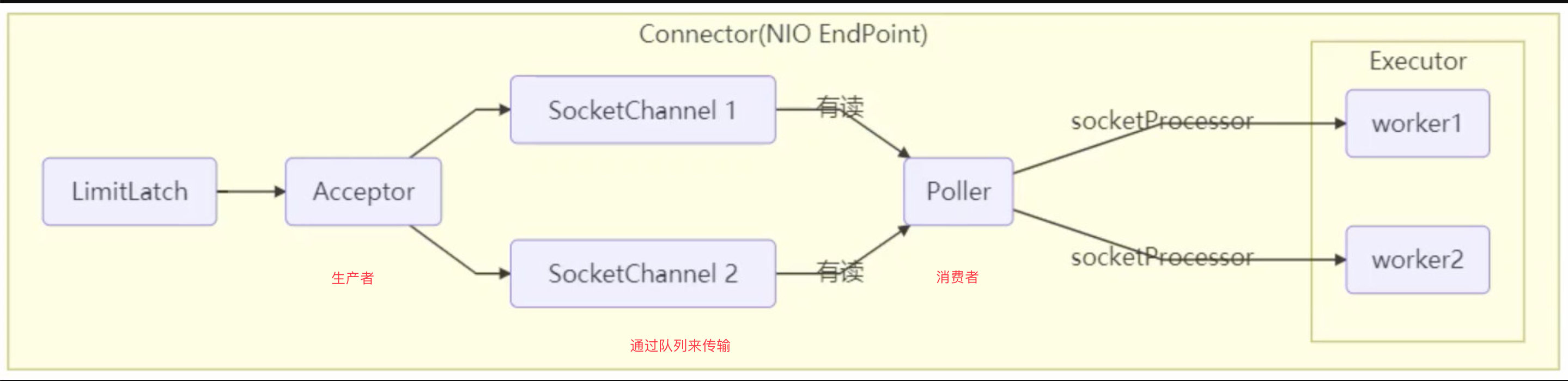
注:我跟了下Tomcat的源码,发现并没有用 ConcurrentLinkedQueue ,可能是版本问题。
7.3.11 CopyOnWriteArrayList
CopyOnWriteArraySet 是它的马甲 底层实现采用了 写入时拷贝 的思想,增删改操作会将底层数组拷贝一份,更改操作在新数组上执行,这时不影响其它线程的并发读,读写分离。 以新增为例:
public boolean add(E e) {
synchronized (lock) {
// 获取旧的数组
Object[] es = getArray();
int len = es.length;
// 拷贝新的数组(这里是比较耗时的操作,但不影响其它读线程)
es = Arrays.copyOf(es, len + 1);
// 添加新元素
es[len] = e;
// 替换旧的数组
setArray(es);
return true;
}
}
其它读操作并未加锁;适合『读多写少』的应用场景
get 弱一致性
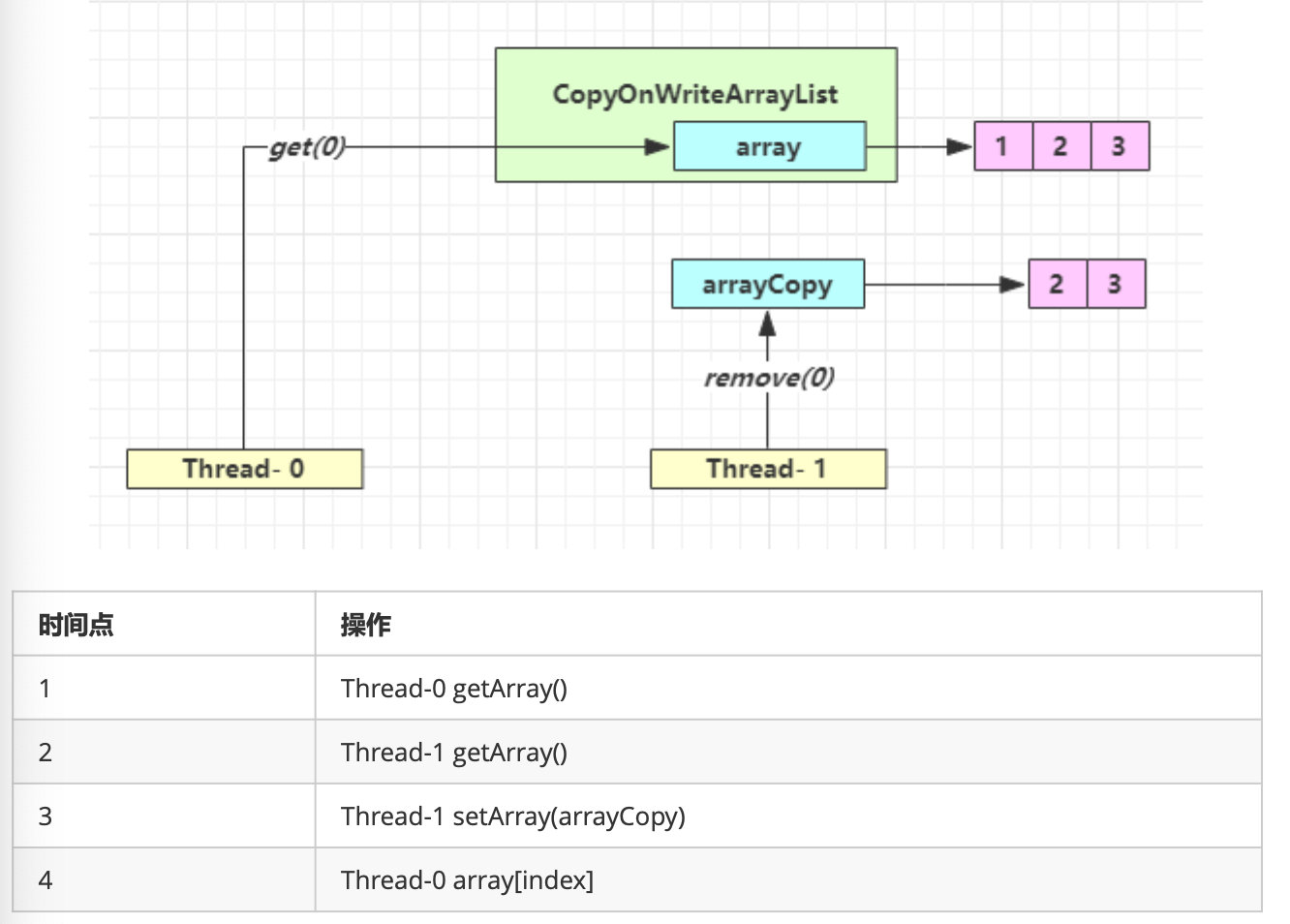
不要觉得弱一致性就不好
- 数据库的 MVCC 都是弱一致性的表现
- 并发高(A可用性)和一致性(C)是矛盾的,需要权衡
 IDEA激活码
IDEA激活码


